Do you know the role that coolant plays in your bike,
and if you need to replace it?
Hello, everyone!
This article will take a look at the importance of coolant.
Coolant is an essential part of maintaining engine performance. Failure to inspect and replace your coolant can not only cause engine malfunctions, but can damage the engine as well.
In this article, we will learn about the role of coolant and proper maintenance methods!
1.The Role of Coolant
1.1 Engine Cooling Systems
There are several types of engine cooling systems, including air-cooled, oil-cooled, and water-cooled. Coolant is used in engines that use a water-cooled system. As it turns out, water-cooled engines are quite mainstream among modern models.

Inside a water-cooled engine are pathways for coolant, which absorb heat from the engine as the coolant passes through them. This heated coolant is then cooled by a radiator located outside the engine, after which the coolant is returned to the engine. This cycle is repeated to maintain proper engine temperature.

1.2 Characteristics of Coolant
The primary role of coolant is to cool the engine, and it possesses several characteristics that allow it to maintain sufficient cooling performance over long periods of time, even under harsh conditions.
Freezing prevention
Generally, water begins to freeze at 0°C, but coolant is designed to not freeze even in cold climates. That is because frozen coolant would not only be unable to circulate through the engine, but it could also damage its pathways.
Rust prevention
Coolant pathways run through the engine and radiator interior, where various metals are used. If rust should develop on those metal parts, the pathways could become clogged. Therefore, coolant is designed to be rust-preventive, helping to keep metal from corroding.
Foaming prevention
Coolant circulates in the pathways, pushed by a propeller-like device called a water pump.
The vigorous propeller rotation could cause foaming if ordinary tap water or another liquid was used, which would prevent the intended cooling performance. Therefore, coolant is designed to be anti-foaming, helping to prevent foaming from happening.
Thus, since coolant has a variety of functions, dedicated coolant must be used instead of ordinary tap water or other common liquids. However, despite its versatility, coolant can gradually decrease in volume or deteriorate over the course of motorcycle use. Therefore, it is important to maintain normal conditions and prevent defects through daily inspections and periodic replacements.
2.Coolant Maintenance Methods
In this section, we will use the CB650R as an example to show how to maintain coolant.
Each model will have a different method, so please check your owner's manual for your particular bike.
Owner's manuals for the various models can also be found at Motopub.

2.1 Coolant Inspection and Replacement Timing
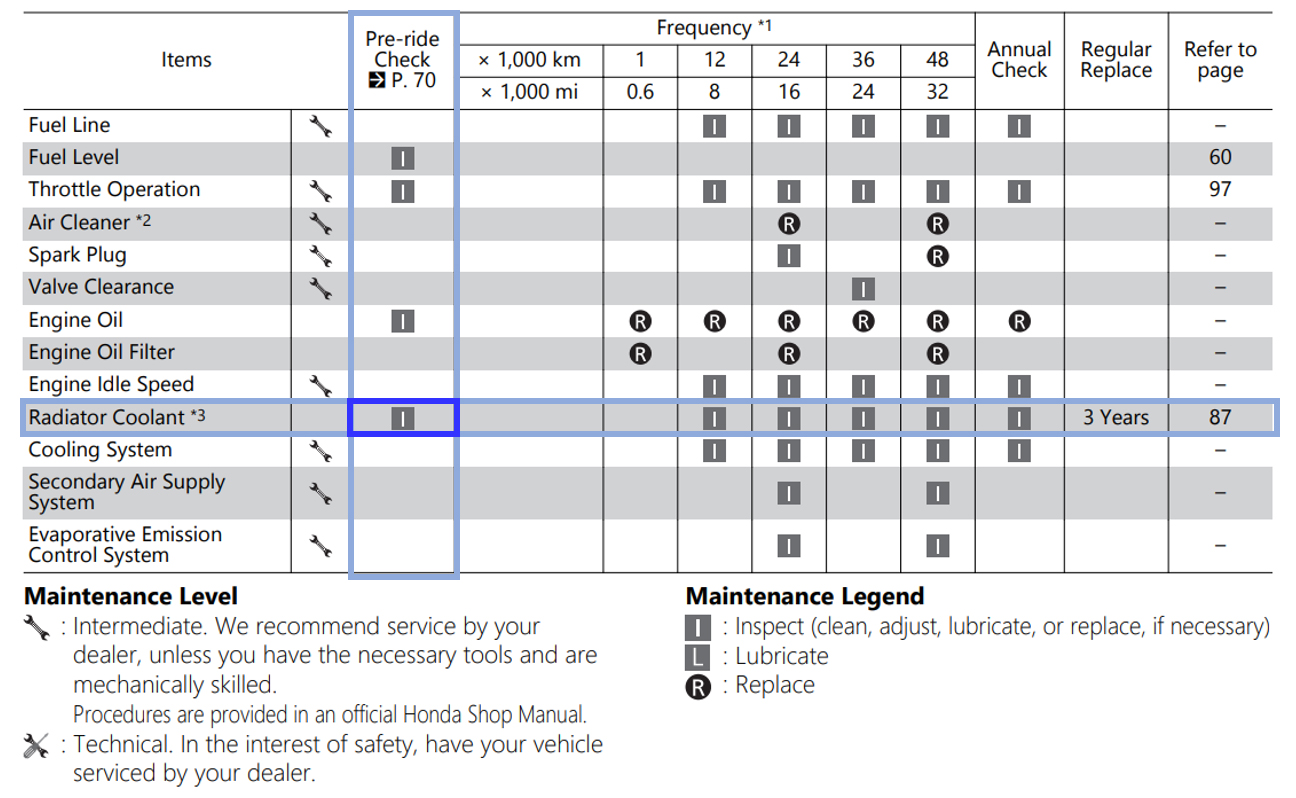
Coolant inspection and replacement timing is listed in the maintenance schedule.
In the example below, we can see that coolant inspection is recommended as a daily Pre-ride Check item as well as a periodic inspection item. The following section will provide a look at how to inspect your coolant. We hope you will give it a try!
We can also see below that coolant replacement is recommended every three years. This is a job that requires specialized maintenance knowledge, so please consult your local dealership.
2.2 Pre-ride Coolant Inspection
In a pre-ride coolant inspection, your main check is of the remaining coolant level.
To avoid burns and other hazards, inspect the engine when it is cool.
For the model we have chosen, you can check the coolant level through the inspection window of the reservoir tank, located around the bottom of the vehicle.
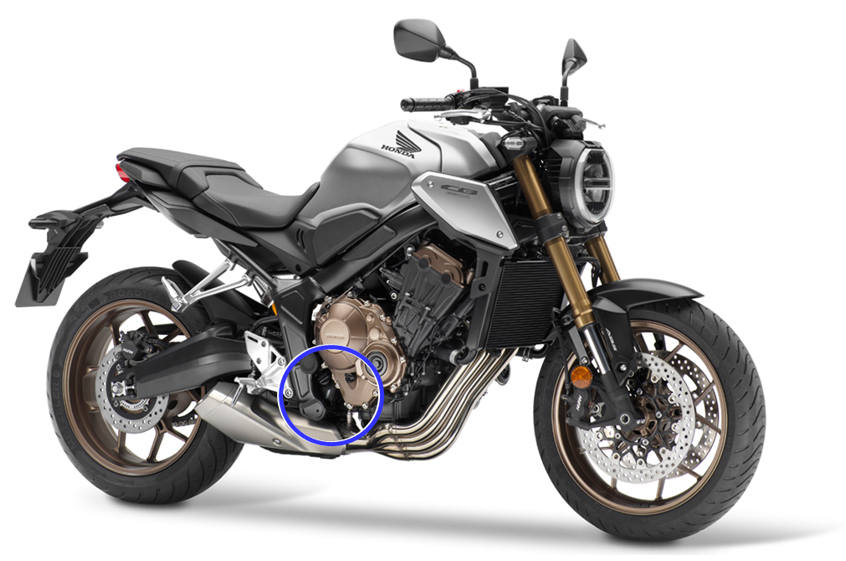

Put the side stand up on a flat surface with a firm foothold and raise the bike straight up so that the body does not fall over.
Once the bike is this position, your coolant levels are okay if they are between the UPPER and LOWER marks on the reservoir tank.
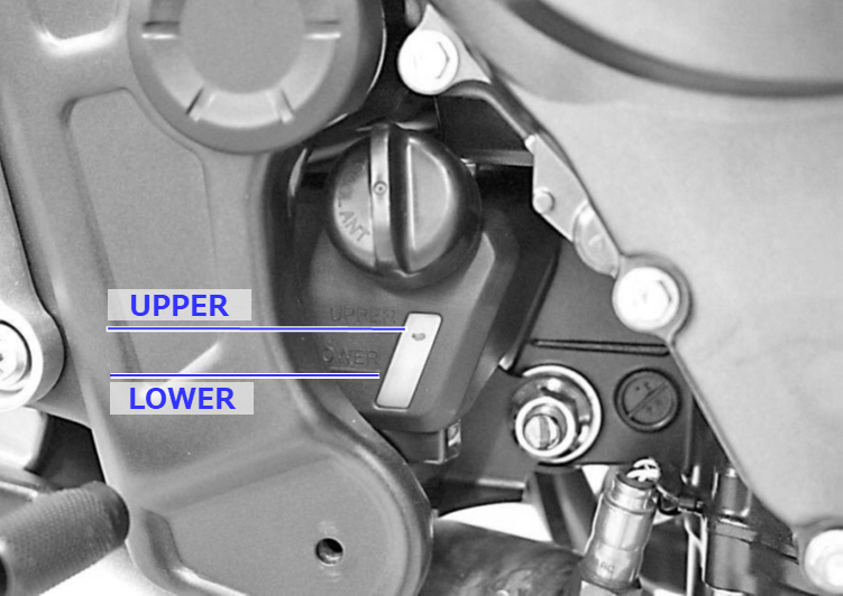
Also check for any coolant leaking or oozing around the engine and radiator. If the coolant is running low or there is no coolant in the reservoir tank, there may be a leak. Please consult your local dealership.
2.3 Refilling Coolant
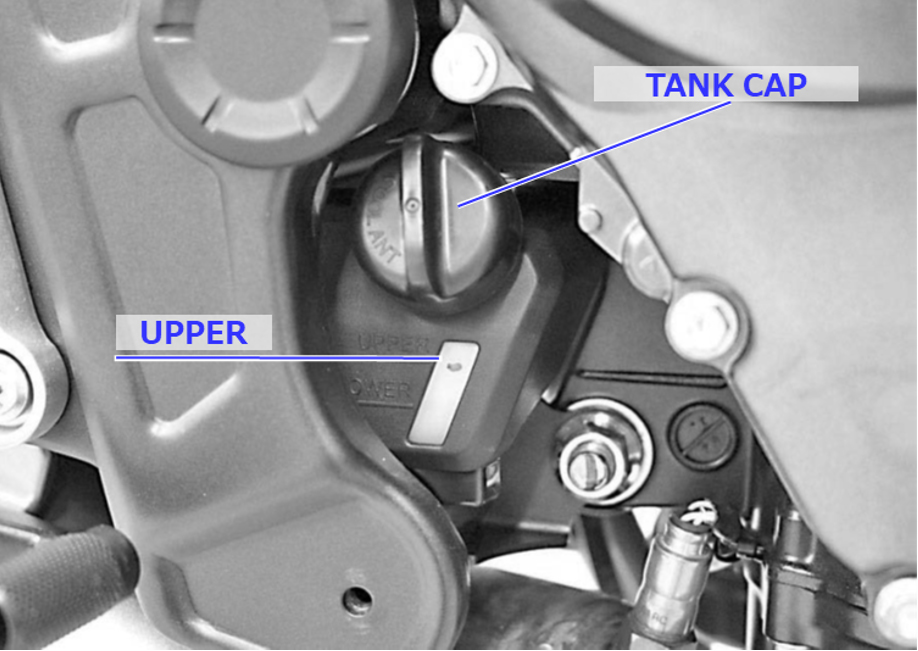
When your coolant runs low, you can refill it through the cap on top of the reservoir tank.
Be careful not to open the cap on the radiator side when you do this.
When refilling coolant, use genuine Honda coolant diluted with distilled water or tap water to the specified concentration.
Remove the reservoir tank cap and refill the tank with coolant, checking coolant levels as you refill with the bike body in a vertical position. Be careful not to exceed the upper limit (marked "UPPER").
Once you have refilled the coolant, securely replace the reservoir tank cap.
If any coolant spills over to peripheral components, be sure to rinse these thoroughly under running water to keep them clean. This will also make it easier to detect problems in the event of coolant leaks or other incidents.
3.Summary
In this article, we took a look at the role of coolant and proper maintenance methods.
Compared to engine oil, coolant is less often replaced and is more often forgotten, but it is still an indispensable element of maintaining your engine's performance.
Note that methods described in this article are only for some models and will vary from model to model.
Please refer to the owner's manual for your bike for details on how to take on maintaining your actual vehicle.
We hope you will stay aware of inspecting your bike on a daily basis to have a more comfortable motorcycle life!
