Honda Begins Testing of Advanced Safety Vehicles and Driving Safety Support Systems on Public Roadways - Honda Cooperating on Development of Driving Safety Support Systems Using Inter-Vehicle and Road-to-Vehicle Communications to Help Reduce Traffic Accidents -
March 24, 2008, Japan
March 24, 2008—Honda Motor Co., Ltd. announced today that it will conduct testing on public roadways of its Driving Safety Support Systems*1 (DSSS) using inter-vehicle and road-to-vehicle communications. The tests, which will be conducted using the “Honda ASV- 4” Advanced Safety Vehicle*2 and other vehicles equipped with advanced safety technology, will be carried out between Monday, March 24, and Friday, March 28, on public roadways in Utsunomiya City, Tochigi Prefecture, Japan.
This round of testing is being conducted as part of a cooperative project that includes Phase 4 of the Advanced Safety Vehicle (ASV) project, conducted under the auspices of the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism’s Road Transport Bureau, and the DSSS, being developed principally by the Universal Traffic Management Society of Japan (UTMS), which is overseen by the National Police Agency. The purpose of the project is to utilize positional information gleaned from communications between motorcycles, automobiles, and road infrastructure to help prevent certain types of traffic accidents which tend to occur frequently.
Honda will conduct these public-road tests using a Forza scooter and an Odyssey automobile equipped with the inter-vehicle communications technologies being developed as part of the the Honda ASV-4, along with two more of the same models equipped with Honda DSSS technologies*3. The objectives of the testing will be 1) to verify inter-vehicle and road-tovehicle communications functions; 2) to verify DSSS functions; and 3) to collect and present data that will contribute to evaluating system effectiveness, thereby contributing to the prevention of accidents involving rear-end collisions, collisions between turning vehicles and oncoming vehicles, and collisions involving turning vehicles with vehicles passing on the inside.
Since late 2007 Honda has also been collecting the necessary data on basic properties affecting the propagation and transmission of radio signals used in inter-vehicle communications. Building on the results of the current round of public-road testing, Honda plans to participate in joint government and private-sector large-scale verification testing scheduled to be carried out in 2008, based on the New IT Reform Strategy (initiated January 19, 2006 by the IT Strategic Headquarters of the Cabinet Office, Government of Japan).
- *1Driving Safety Support Systems (DSSS): Systems that provide the driver with visual and audio information on the surrounding traffic environment to alert the drivers of possible driving-related dangers and facilitate greater attentiveness, promoting a more relaxed driving environment and preventing traffic accidents.
- *2Advanced Safety Vehicle (ASV): A vehicle equipped with systems using advanced technologies to assist the driver in safe driving. The ASV project, conducted under the auspices of the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, involves the cooperation of industry, academia, and government. It is currently in Phase 4 (2006~2010).
- *3The motorcycle used in DSSS testing is utilized for camera detection purposes.

Honda ASV-4

Honda DSSS
Overview-Public-Road Verification T esting of Honda ASV-4 and Honda DSSS in Tochigi, Japan
The public-road verification testing in Tochigi, Japan will be carried out by four companies: Nissan Diesel Motor Co., Ltd., Fuji Heavy Industries Ltd., Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation and Honda Motor Co., Ltd.

ASV-4 logo

Driving Safety Support Systems
UTMS Association
DSSS logo
<ASV/DSSS verification test objective>
The system will use communications infrastructure to assist in providing positional information on difficult-to-spot motorcycles that may not be detected by independent onboard sensors.
<System functions subject to verification testing>
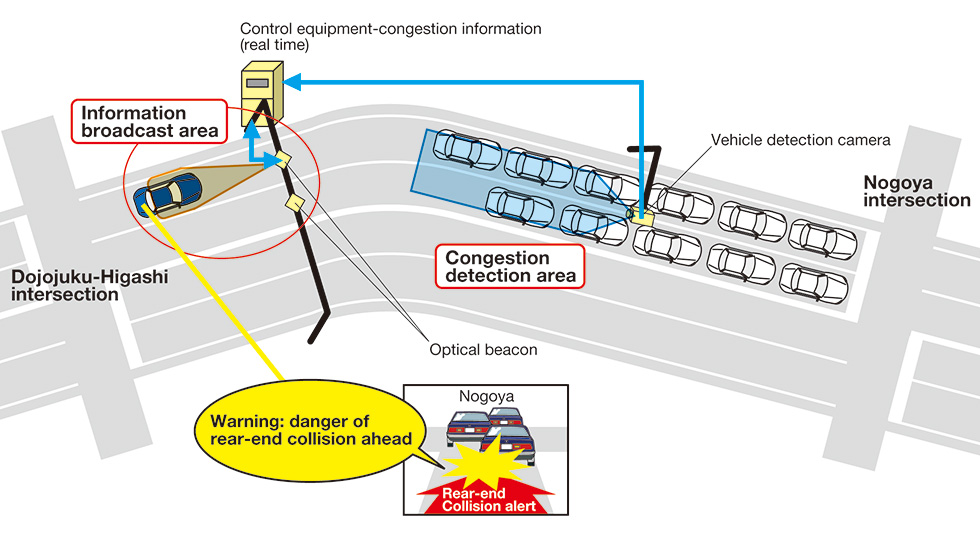
(1)Rear-end Collision Avoidance Assistance Information System (DSSS)
Objective:
- To assist in preventing rear-end collisions in poor-visibility conditions by providing positional information on vehicles stopped in the road ahead.
Desired effects:
- Reduced incidence of rear-end collisions.
- Prevention of traffic accidents caused by inattentive driving (by compensating for errors in recognition and judgment).
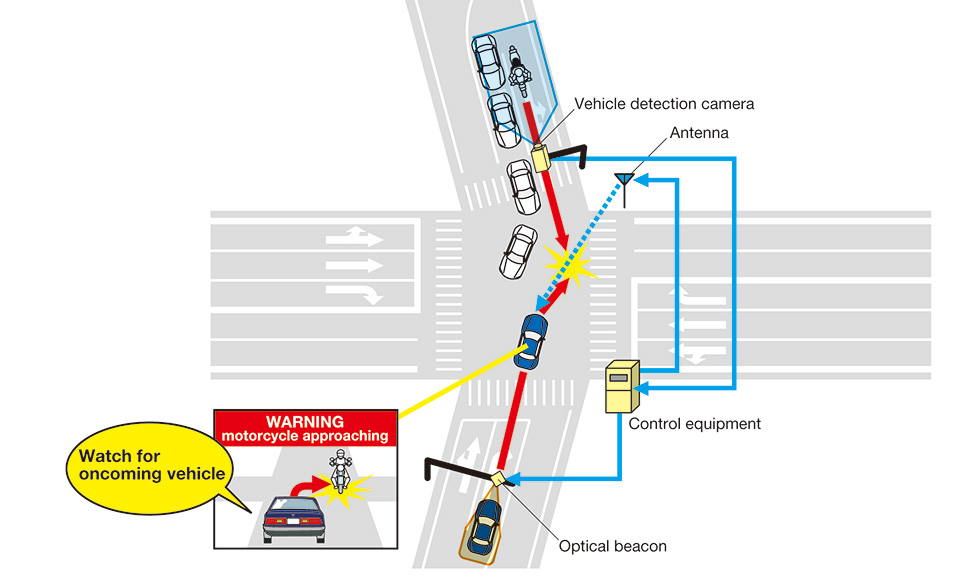
(2)Cross-Traffic-Turning and Oncoming Vehicle Collision Avoidance Assistance Information System (ASV/DSSS)
Objective:
- To assist in preventing collisions between vehicles turning across traffic and oncoming vehicles by providing vehicles turnings at signal-controlled intersections with positional information for difficult-to-spot oncoming vehicles.
Desired effects:
- Reduced incidence of collisions between turning vehicles and oncoming vehicles (prevention of accidents caused by perceptual error or miscalculation; compensation for errors in judging the speed and distance of motorcycles and facilitation of awareness of the presence of motorcycles).
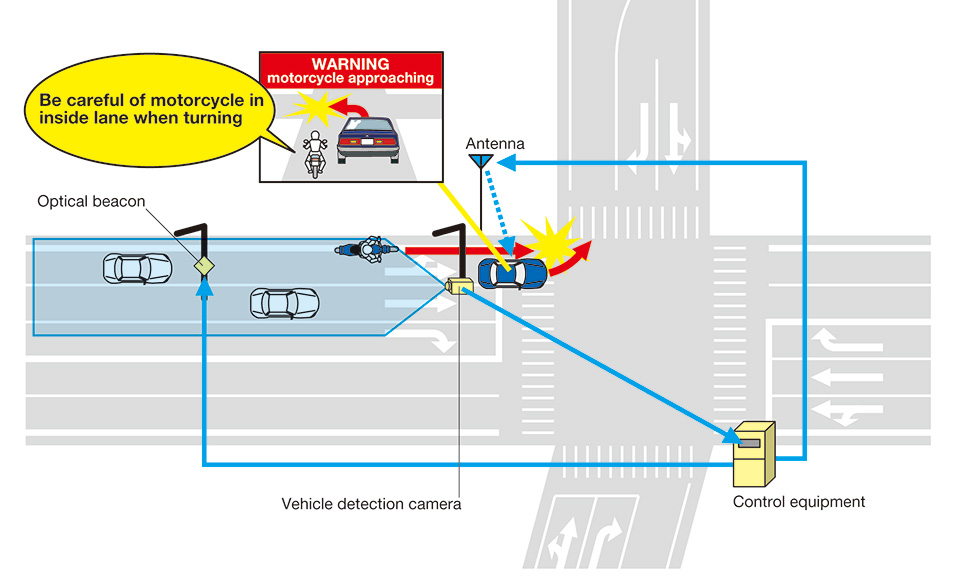
(3)Inside-Lane-Turning Vehicle Collision Avoidance Assistance Information System (ASV/DSSS)
Objective:
- To assist in preventing collisions between motorcycles passing on the inside and vehicles turning at signal-controlled intersections by providing positional information on difficult-to-spot vehicles approaching from the rear.
Desired effects:
- Reduced incidence of collisions with motorcycles passing on the inside during turns (prevention of accidents by providing supplementary information on vehicles in blind spots).