Water
Regarding water resources as natural capital, water-related problems are becoming more serious, such as floods and droughts caused by the effects of climate change and the expected increase in water demand due to the growth of the world’s population.
Honda recognizes the potential impact on local communities and downstream water resources in areas where we draw water and is committed to water conservation.
We select regions that harmonize with surrounding water resources and conduct our corporate activities in accordance with environmental assessment regulations in each country.
With the aim of achieving zero industrial water withdrawal by 2050, we are also working to minimize water use, such as utilizing recycled water and water conservation, taking into account local conditions.
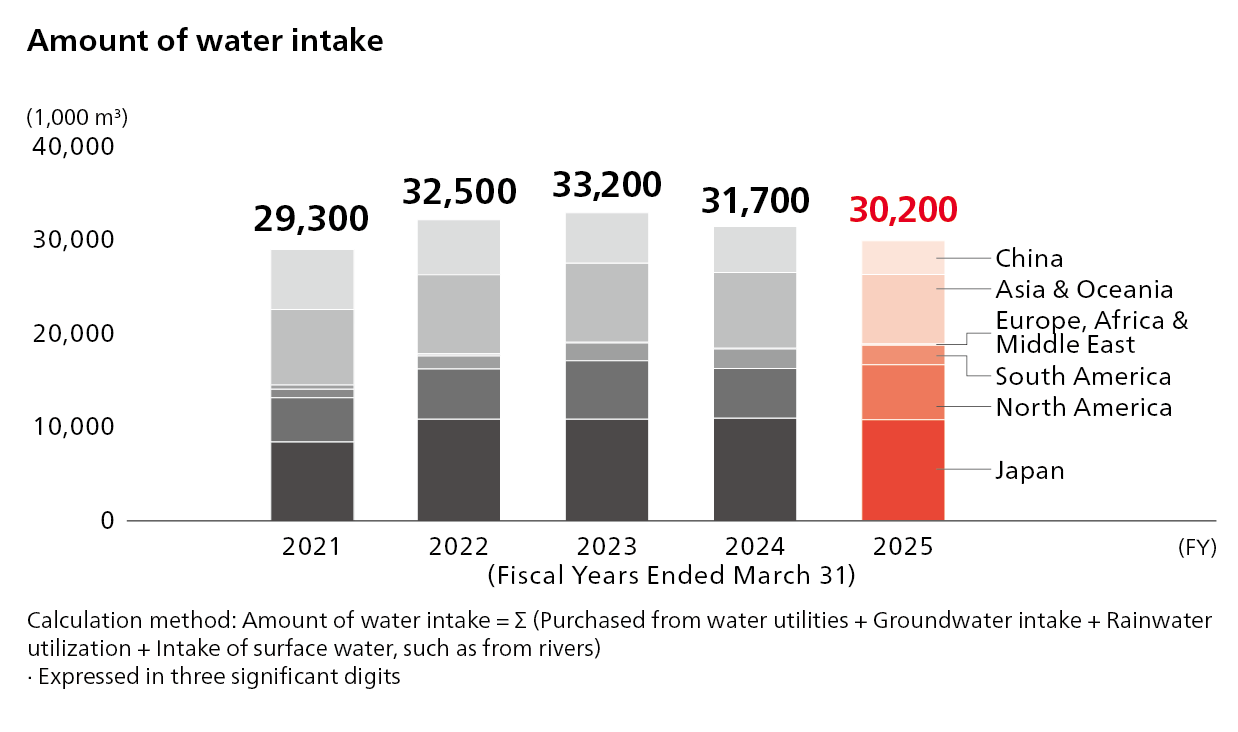
In addition, with an eye on supply risks that could affect our businesses and depletion risks that could affect local communities, we aim to reduce the total amount of water withdrawn across all Honda corporate activities.
Setting New Targets with a View to 2050
For more fundamental issue solving, as one of the interim targets linked to our ideal state by 2050, we have set new KGI and target to reduce industrial water withdrawal by 12% by the Fiscal Year Ending March 31, 2031.
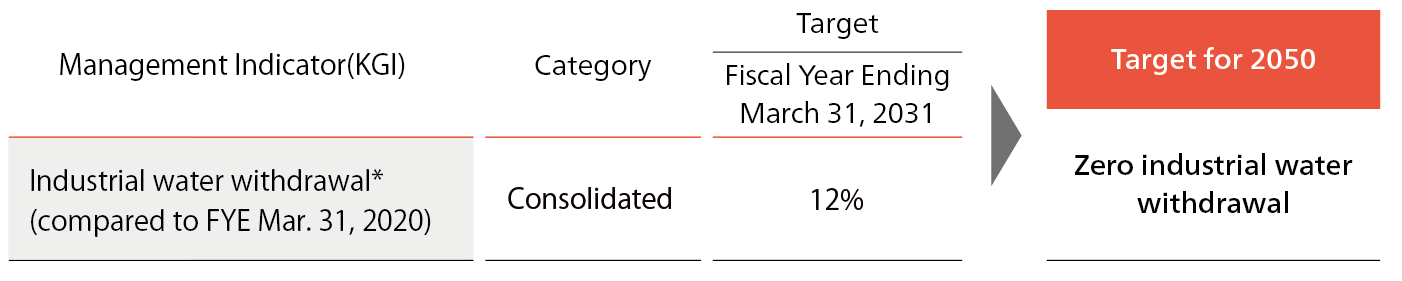
- Industrial water withdrawal: The annual amount of water withdrawn that is directly used in product development and manufacturing in corporate activities. This indicator excludes domestic water use, such as drinking water and handwashing facilities for associates, which are provided as safe water, sanitation facilities, and hygiene practices (WASH: water, sanitation, and hygiene) under the Alliance for Water Stewardship (AWS) standard, which requires the provision of hygienic water and facilities.
Water is a resource that is unevenly distributed by region and season, etc. At our production sites that use a large amount of water, we verify and identify risks in terms of water resources, groundwater, drought, water quality, regulations/rumors, etc. in the site areas using evaluation indicators such as AQUEDUCT and Water Risk Filter. We are thus promoting risk-based initiatives.
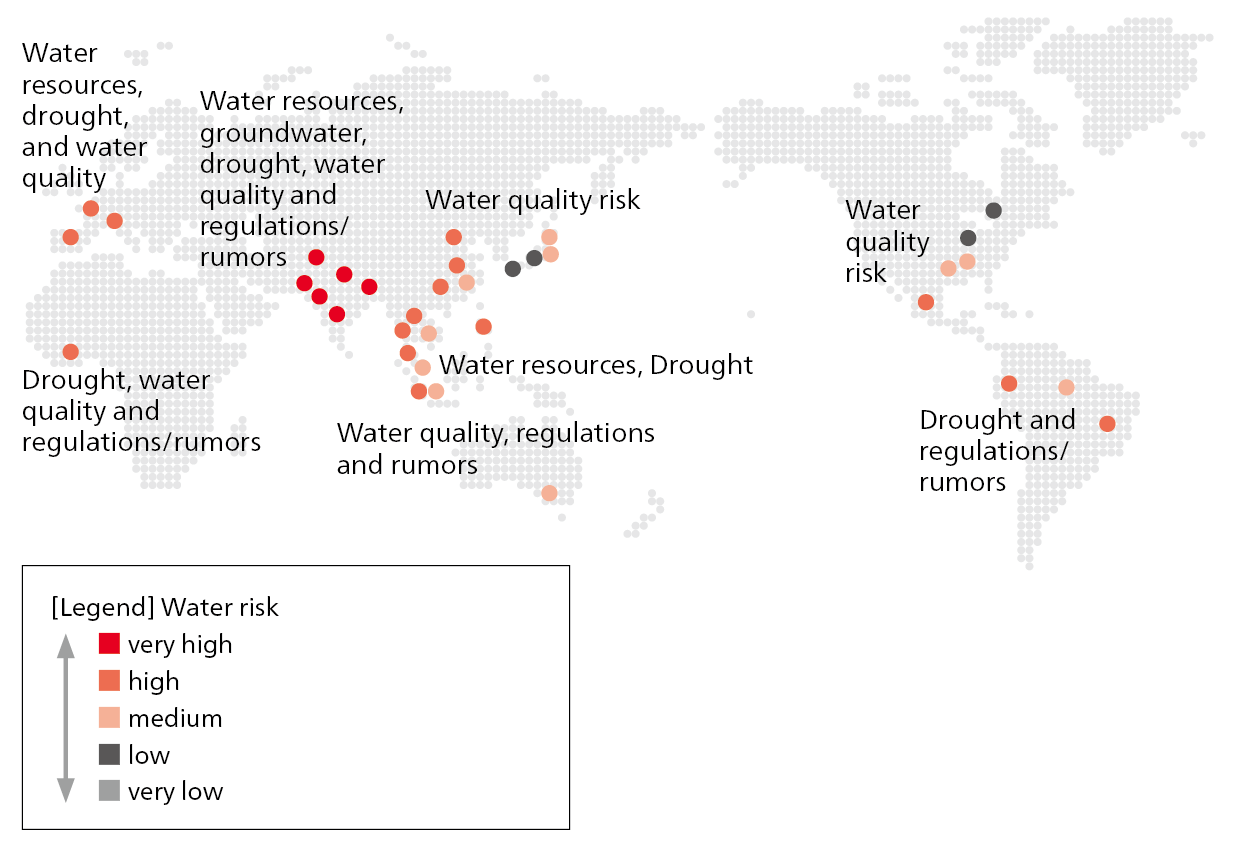
Honda has prioritized the introduction of a water recycling system at the Celaya Auto Plant of Honda de Mexico S.A. de C.V. in Mexico, the Tapukara Plant of Honda Cars India Ltd. in India, and the No. 2 Plant of GAC Honda Automobile Co., Ltd. in China, where the water risk is particularly high.
■Recycled water consumption (global manufacturing sites)
3.16 million m3/year (approximately 14% of the total amount used)
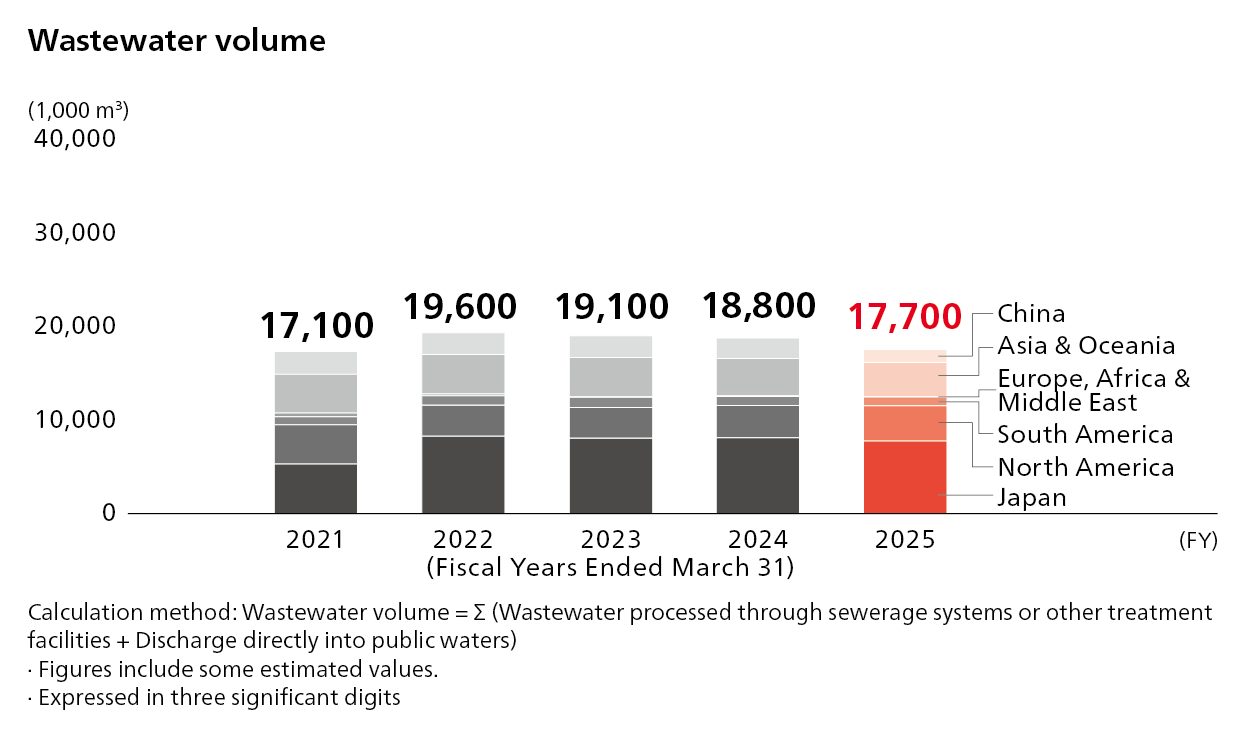
Regarding wastewater, no water sources are affected by wastewater from Honda facilities since it treats wastewater and discharges treated water in accordance with applicable laws and regulations of each country, and the amount of wastewater is appropriately being managed.
Going forward, taking into consideration the characteristics and challenges of water resources in each region, we will continue to conduct water risk assessments at each production site, as well as emphasize consideration for biodiversity and contribute to the conservation of water environments and local communities in upstream and downstream areas around our sites.