ATR and Honda Successfully Develop New Brain-Machine Interface Creating Technology for Manipulating Robots Using Human Brain Activity
May 24, 2006, Japan
May 24, 2006- Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute International ("ATR") and Honda Research Institute Japan Co., Ltd. ("HRI") have collaboratively developed a new "Brain Machine Interface" ("BMI") for manipulating robots using brain activity signals. This new BMI technology has enabled the decoding of natural brain activity and the use of the extracted data for the near real-time operation of a robot without an invasive incision of the head and brain. This breakthrough facilitates greater possibilities for new types of interface between machines and the human brain.
The idea of this BMI technology is based on a highly acclaimed article titled "Decoding the perceptual and subjective contents of the human brain" by Dr. Yukiyasu Kamitani, a researcher at ATR Computational Neuroscience Laboratories, which recently appeared in a leading science journal, Nature Neuroscience. For this study, Dr. Kamitani was named by Scientific American magazine as Research Leader, with his collaborator Dr. Frank Tong at Vanderbilt University, within the 2005 Scientific American 50 - the magazine's prestigious annual list that recognizes outstanding acts of leadership in science and technology. HRI and ATR have developed the article's theory into a system for real-time brain activity decoding and robotic control.
This research reveals that MRI-based neural decoding can allow a robot hand to mimic the subject's finger movements ("paper-rock-scissors") by tracking the hemodynamic responses in the brain. Although there is an approximate 7-second time lag between the subject's movement and the robot's mimicking movement, the researchers succeeded in gaining a decoding accuracy of 85%.
This technology is potentially applicable to other types of non-invasive brain measurements such as the brain's electric and magnetic fields and brain waves. By utilizing such methods, it is expected that the same result could be achieved with less time lag and more compact BMI system devices.
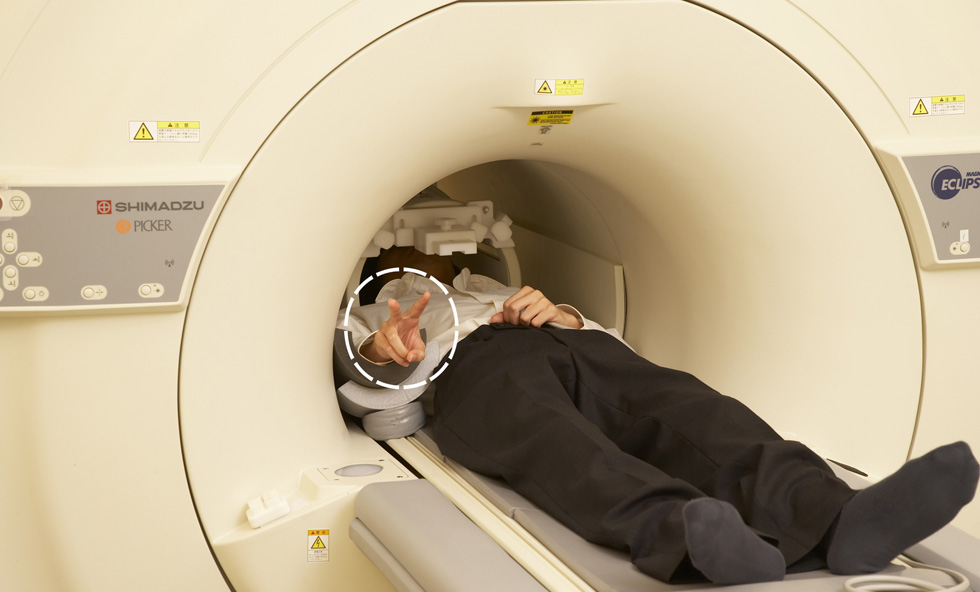
Scanning Brain Activity Using MRI
(showing “scissors”)
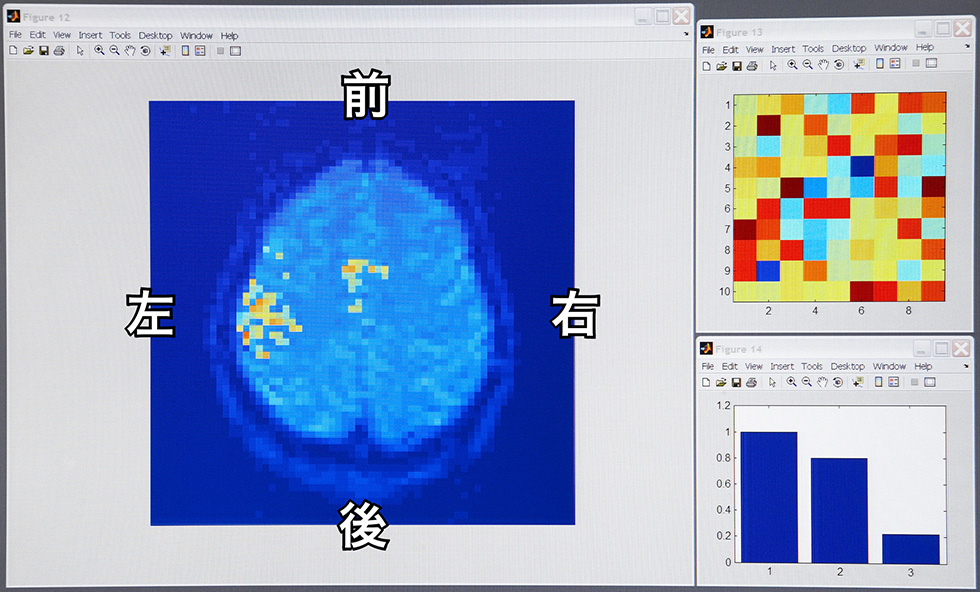
Analysis of a brain image by a computer program
(Left) Active brain areas
(Upper right) Extracted brain activity patterns
(Lower right) Pattern classification processing

Simulation of the subject’s
hand movement by a hand shaped robot
- Experimental Procedures of the Newly Developed BMI
- Outline of Experimentation:
The subject in an MRI scanner makes a finger gesture, “paper,” “rock” or “scissors,” while the changes in his/her hemodynamic responses associated with brain activity are monitored every second. Specific signals generating paper-rock-scissors movements are extracted and decoded by a computer program, and the decoded information is transferred to a hand-shaped robot to simulate the original movement performed by the subject.
- BMI
While conventional machine-interfaces are operated using button switches controlled by human hands or feet, BMI uses brain activity measured by various devices and allows non-contact control of the terminal machines. Implanted electrode arrays, and brain waves have been commonly used.
- Features of the new BMI Technology Developed by ATR and HONDA
The system is aimed for applications of BMI to everyday life, without need for surgery or intensive user training.
- 1)No Surgery Required
In conventional BMI research efforts led by U.S. neuroscientists, invasive technologies, including electrode array implants, have been used. If advanced non-invasive BMI becomes available, users will be free from the physical burden of a surgical procedure. This research accomplishment demonstrates the possibility of such a useful application.
- 2)No Specific Training Required
Conventional non-invasive BMI required the user to undergo intensive training in order to generate detectable brain activities. For example, as the brain activity associated with an intention, say "Yes", is very hard to track, the user is instructed to perform a mental task that is irrelevant to the mental state but associated with easily detectable brain activity such as mental calculation. The user must learn to control such brain activity to express an intention. The new BMI technology is different in that natural brain activity associated with specific movements can be decoded without using alternative brain activity. The experiment revealed that paper-rock-scissors movements were decoded directly from an untrained subject's real-time brain activity. This is an outstanding breakthrough in brain decoding technologies .
To achieve real-time brain activity decoding and robotic control, a system provided by the Computational Brain Project of Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST-ICORP: Research Supervisor (Japan): Dr. Mitsuo Kawato, Research Supervisor (U.S.): Dr. Christopher Atkeson) was used for simulation of the subject's movement by a robot hand. The ATR Brain Activity Imaging Center (BAIC) provided support in areas related to the MRI machines.