Honda’s R&D Facilities Chapter 1
Honda’s R&D Facilities: Manufacturing Starts Here
Honda’s R&D Facilities Chapter 1

Why Split Off R&D into an Independent Division?
Honda split its research and development function from its sales and marketing function to create an independent division. The change was made to maintain and expand the company’s approach to manufacturing since foundation, that “Utilizing our technology to help people.” Development at the time of founding was led by the genius of one man, Soichiro Honda, but to ensure the company could continue as an organization developing technologies that were useful to people, they had to create many more Soichiro Hondas to take on challenges as a group.
Honda split off its R&D function so that the creation of new value would be entrusted to a group rather than to an individual. While cooperating closely with other divisions, Honda’s R&D division is able to conduct its work in an environment that enables creative thinking without being influenced by short-term business performance.
Honda R&D Co., Ltd., established in 1960 (photo taken in 1961)

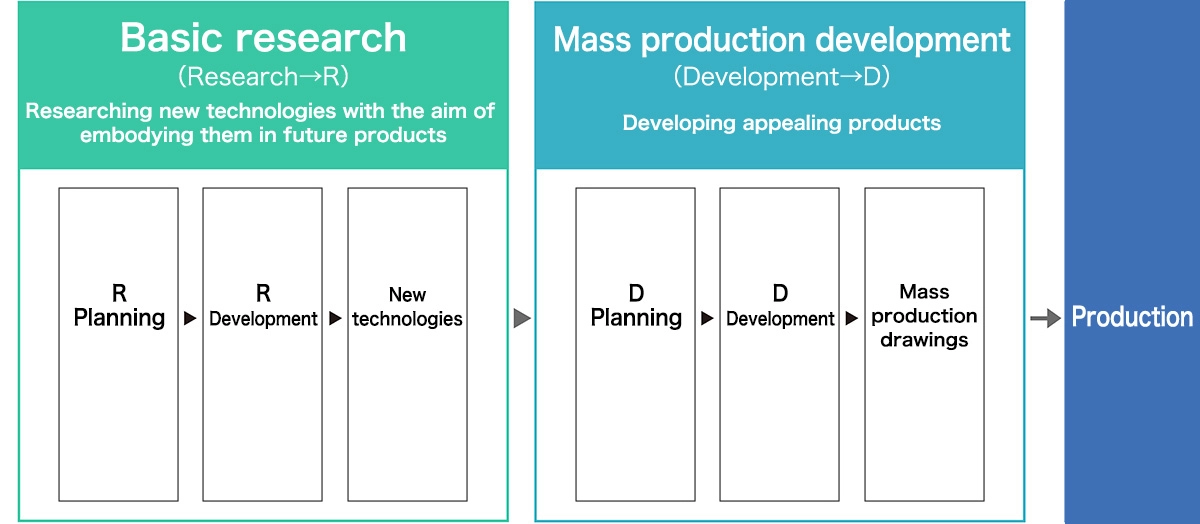
From initial planning to delivery to the customer, products pass through a process that includes planning, development, production, and sales. In 1974, Honda developed the SED development system out of the conventional system of bringing products to market at the time, which was like a relay race from development to production to sales. In the SED system, with S standing for sales, E standing for production and production engineering, and D standing for research and development, these three functions operate simultaneously. The aim was to reflect market and production floor opinions directly in development and to organically connect to the development of products that were pleasing and satisfying to customers.
The separate planning divisions of the automobile, motorcycle, power products, and other divisions are tasked with planning products that will be useful to people and society. Working in conjunction with product planning are the development divisions, which are separated into two functions. The first is a basic research function that researches new technologies from the long-term perspective with the aim of embodying them in future products. The second is a mass production development function that conducts development with the aim of bringing planned products to reality. In the narrow sense, the functions are research (R) and development (D).
Looking at automobiles, for example, R&D is conducted across a myriad of themes. They include hybrid systems that strike a perfect balance between fuel economy and driving performance, next-generation powertrains for electric vehicles and fuel cell battery systems, transmissions and other drive systems, bodies and chassis that improve driving performance, electric and electronic control systems, active safety and collision safety, and automated driving and intelligent systems.
Structure of R&D at Honda
Honda’s Thoughts on R&D: “Utilizing our technology to help people.”
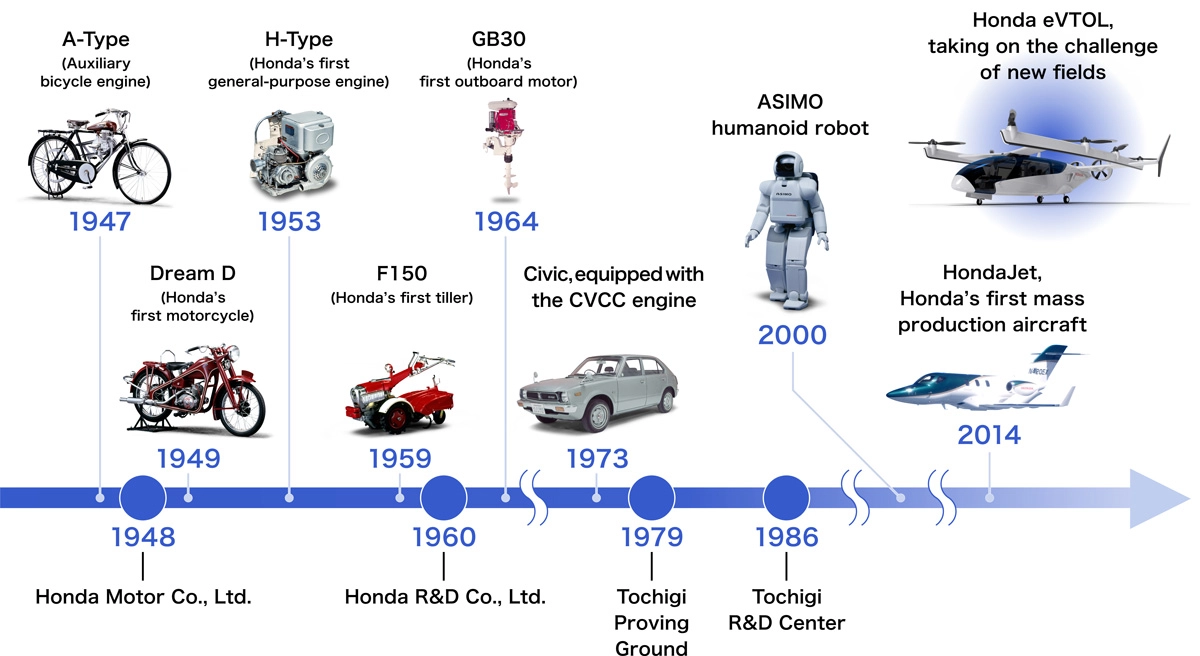
The history of technological development at Honda has maintained a focus on contributing to the development of the mobility society through unique technologies by anticipating the needs of the times. In September 1946, soon after the war, founder Soichiro Honda started attaching auxiliary engines to bicycles using wireless radio generator engines left at military factories. This is considered to be the origin of the “Utilizing our technology to help people.” approach.
Founded as a company making products from these bicycle auxiliary engines, Honda started producing the A-Type engine, an original design, in 1947. Then in 1949, it started making full-fledged motorcycles, producing everything internally from the frame up, and launched its Dream D motorcycle. In 1953, it launched producing the H-Type engine as its first general-purpose engine. Taking advantage of the technologies and production systems developed through motorcycle production, it launched the F150 in 1959 as the company’s first tiller for farming.
In 1964, Honda launched its first outboard motor, the GB30 equipped with a four-stroke engine and developed in line with the philosophy of founder Soichiro Honda that “watercraft should not pollute the waters they ply.” In 1972, the company completed development of its CVCC engine, a low-emission engine that met the Muskie Act (U.S. Clean Air Act) standards that automakers around the world had claimed was impossible, and it installed the engine on its Civic model cars.
In 2000, Honda unveiled the ASIMO humanoid robot designed to realize the dream of enriching human society. In 2015, it established its HondaJet mass production system for small business jets that would expand the joy and freedom of mobility to the skies. It is now in the process of developing electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft to make the sky even more accessible.
Powered by gas turbine generators and batteries, eVTOL aircraft make use of an unbroken chain of knowledge built up through Honda’s history of R&D. Including hybrid technologies developed through racing activities, HondaJet aircraft engine technologies, and experience acquiring type certification, all this knowledge is being used to develop lightweight structures, ultra-high rpm generators, and other technologies. As a company with technologies acquired through its involvement with mobility on land and in the skies, Honda has developed a range of unique mobility options that anticipate the needs of the times.
Examples of development that embody the “Utilizing our technology to help people.” approach
R&D Facilities Creating the Joy and Freedom of Mobility
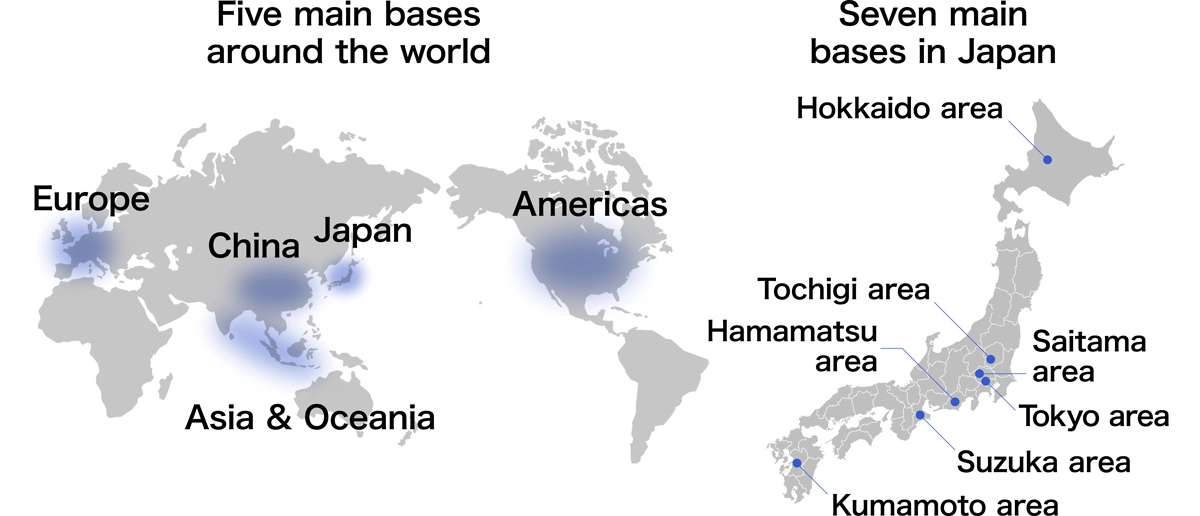
Honda has established R&D bases around the world to ensure research and development of these diverse mobility options is rooted in needs of customers in each region. Those regions are Japan, the Americas, China, Asia & Oceania, and Europe. Its seven main bases in Japan are in the Hokkaido, Tochigi, Saitama, Tokyo, Hamamatsu, Suzuka, and Kumamoto areas.
Honda’s R&D bases
Of these, the Tochigi Proving Ground was established in 1979 and the Tochigi R&D Center was established in 1986 to create an R&D facility and proving ground on a roughly 2.13 square-kilometer site measuring 1,360 meters east-west by 1,860 meters north-south.
Located on the eastern side of the site, the proving ground is used for a range of test driving. Buildings for R&D are arranged in vertical and horizontal rows across the rest of the site, with the design functions located in and extending horizontally from the middle. The research functions are arranged vertically from there to enable prompt feedback of test results to the design functions, thereby creating an efficient arrangement that facilitates problem solving.

Honda uses its various R&D facilities to take on the challenge of providing the joy and freedom of mobility to everyone around the world. Enabling it to overcome a range of difficulties and provide considerable value to the world through many mobility options, Honda’s R&D facilities are where the manufacturing really starts at Honda. New technologies and new products are being created there, right at this very moment.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd. and Honda R&D Co., Ltd. (Tochigi)

TechnologyHonda’s R&D FacilitiesHonda’s R&D Facilities: Manufacturing Starts Here