Electric Motorcycle “Honda WN7”
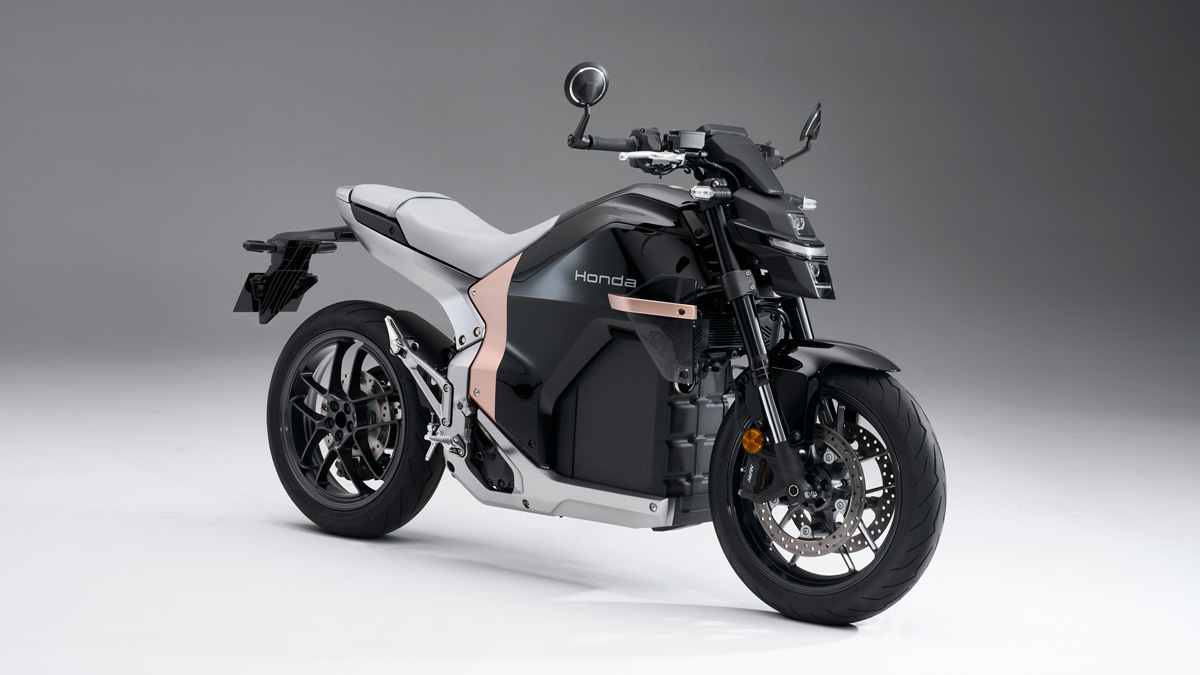
Honda has unveiled its first electric motorcycle, “Honda WN7” (hereinafter “WN7”), in Europe. The WN7 is the production model of the “EV Fun Concept” exhibited at EICMA 2024 in Milan, Italy, and will be exhibited at EICMA 2025 (open to the public from November 6 to 9).
The grand concept of the WN7 is “Be the Wind, Listen to the Sounds of Nature, and Feel the Earth.” As an electric motorcycle, the WN7 allows riders to hear sounds that they could not hear with an internal combustion engine (ICE) motorcycle, like the voices of people while riding through the city or the sound of water splashing when stepping in a puddle. Being electric means it can deliver a satisfying feeling of acceleration and deceleration, offering a quiet and smooth riding experience with minimal vibration and noise. It also produces no exhaust emissions, enabling it to become a presence in harmony with nature.
A Chassis Designed to be Lightweight, Slim, and Easy to Handle
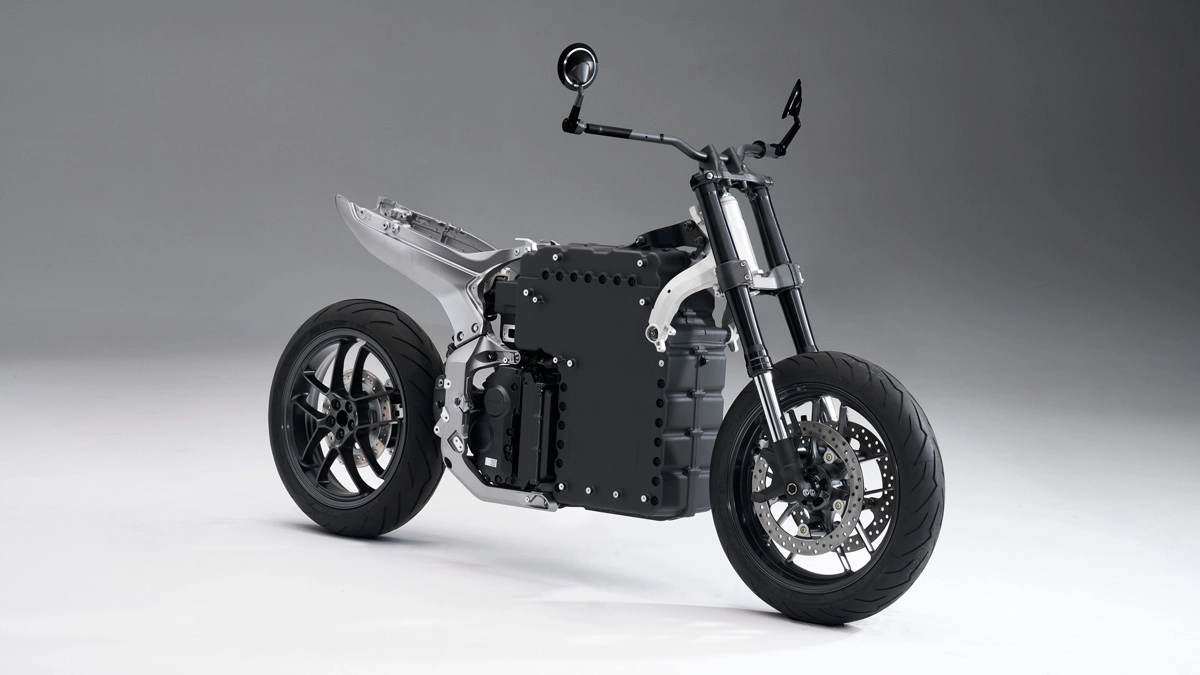

The WN7 targets active young people living in European cities, emphasizing lightness and ease of handling in daily riding situations. The weight of the completed model is 217 kg, achieving light handling that allows control with confidence even on congested roads. An appropriate caster angle has been set, aiming to achieve a slim body that is only possible with an electric motorcycle. In addition, ease of handling has been achieved by lowering the center of gravity height, securing an appropriate wheelbase and handlebar turning angle, and considering a slim body and seat height that ensures solid footing.
Placing wide parts on the top and where the rider straddles forces a wide-legged riding position, worsening footing and raising the center of gravity. After much consideration, the seat height was set to 800 mm to ensure solid footing, and the pivot bracket from the seat was designed to be slim. For ease of handling in daily riding situations, the wheelbase has been set to 1480 mm and the handlebar turning angle to 35 degrees. After setting these specifications to achieve lightness and ease of handling, the placement of components and the frame structure necessary to realize these specifications were considered.
This resulted in a front-rear split configuration without a main frame. ICE motorcycles typically feature a frame structure that supports the engine, transmission, and swingarm supporting the rear wheel. Attempting to maintain this structure by running a frame through the front and rear would place the frame alongside the battery pack required to ensure a driving range exceeding 130 km, making a slim design impossible. It was also undesirable from the perspective of achieving the target weight of the completed model.
However, Honda made a breakthrough with the WN7 by adopting a front-rear split configuration to address the challenges of slim packaging and completed car weight. The battery pack, which forms an inverted L-shape when viewed from the side, is positioned in the center of the motorcycle, with the head pipe holder attached to the front and the pivot bracket attached to the rear to form the skeleton. This has helped achieve the target weight of the completed vehicle by contributing to slim packaging and light and agile handling.
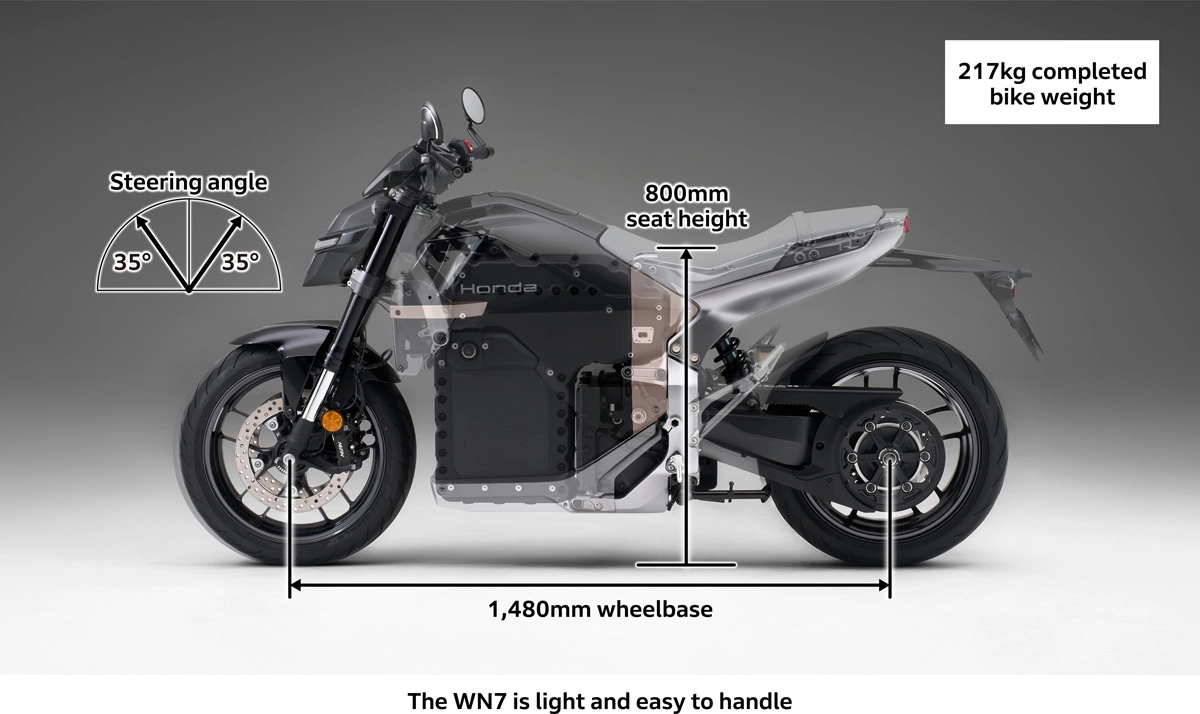

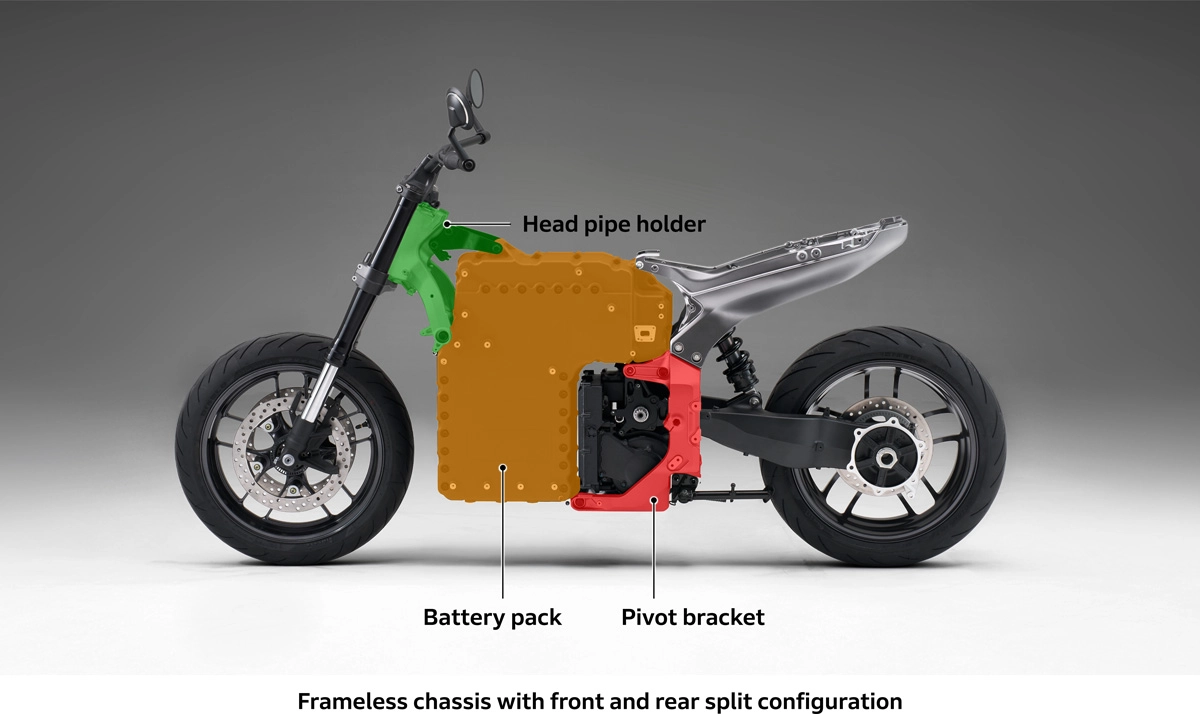
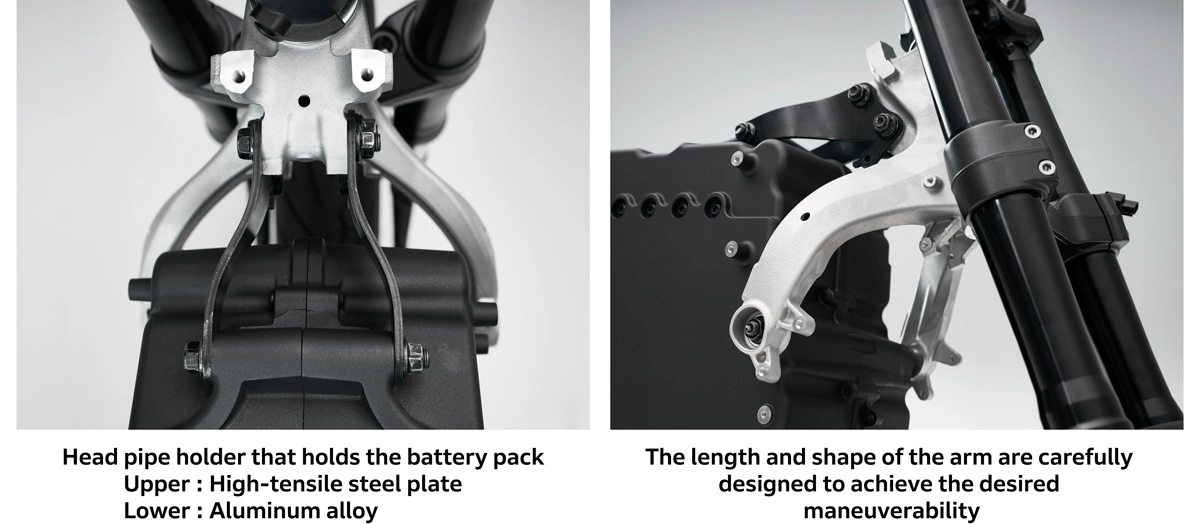
The challenges when adopting a front-rear split configuration for the head pipe holder, battery pack, and pivot bracket were achieving the desired handling characteristics and minimizing dimensional variation. With a conventional frame structure, the long dimensions made it possible to shape the riding feel by allowing the frame to flex. However, with the front-rear split configuration, the nearly rigid battery pack is sandwiched between the front frame and pivot bracket, requiring the riding feel to be shaped by the short head pipe holder and pivot bracket.The lower section of the aluminum alloy head pipe holder, which forms an inverted Y-shape when viewed from above, features elongated left and right arms that are designed to flex smoothly. If designed in a linear shape, it would tend to give off a tense feeling, so the idea was to intentionally divert the forces. Conversely, high tension steel plates have been used for the upper arms. By intentionally creating a curved shape to sandwich the battery pack within, a deliberate load transfer loss was introduced, allowing flex and bending to shape the riding feel.
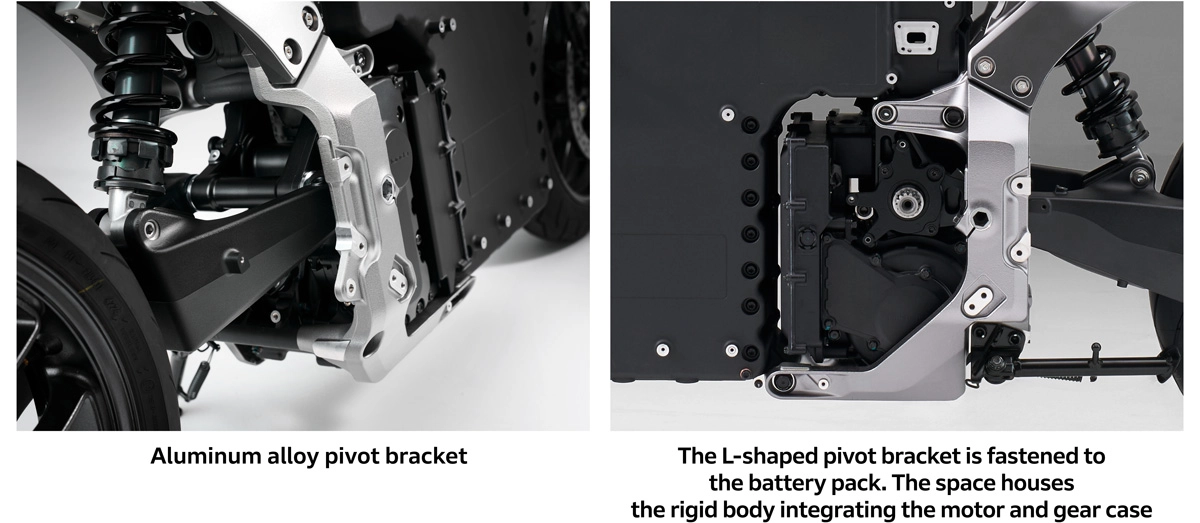
The pivot bracket is made of aluminum alloy. The fastening span was set as wide as possible while still providing good riding position and footing, efficiently ensuring rigidity while establishing favorable flexibility. When the pivot bracket, which forms an L-shape when viewed from the side, is fastened to the battery pack, a space is created between it and the inverted L-shaped battery pack. This space accommodates the rigid aluminum alloy body consisting of the motor and gear case. Fastening the motor and gear case to the pivot bracket to form a single unit aimed to achieve an effect that is similar to the pivot upper/lower cross members in ICE vehicles.
In designing the front-rear split configuration, Honda leveraged its longstanding expertise in ICE vehicle development—know-how and technology honed over years on how the frame should move and how to make it move—and further evolved the idea. This approach overcame unfavorable conditions to achieve the desired handling characteristics.
If dimensional variations in the components that make up the skeleton occur, there could be issues like misaligned caster angles, making it impossible to guarantee performance specifications. Therefore, controlling dimensional variation is crucial. However, since the WN7 was designed as a front and rear split configuration, it’s difficult to achieve the same dimensional variation range with conventional manufacturing methods. Consequently, the head pipe holder and pivot bracket were manufactured without welding, which can cause distortion, and instead were machined to ensure dimensional accuracy. In addition, adopting positioning pins, specifying the reference position of the drawing dimensions, and specifying the order of fastening with the battery pack ensures that the desired performance is delivered to the user.
Pursuit of Quietness and Usability
The WN7 features a belt drive system rather than a conventional chain drive system. Belt drive systems are significantly quieter than conventional chain drive systems, making them one of the technologies supporting the WN7’s grand concept: “Be the Wind, Listen to the Sounds of Nature, and Feel the Earth.”
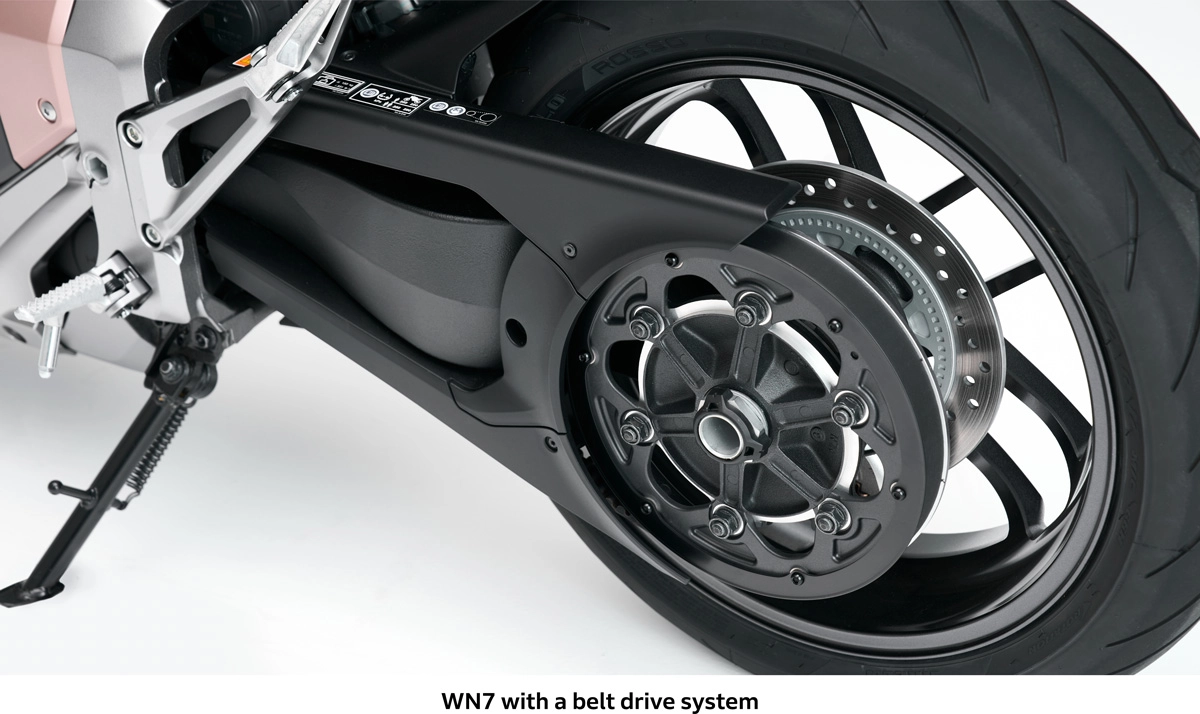

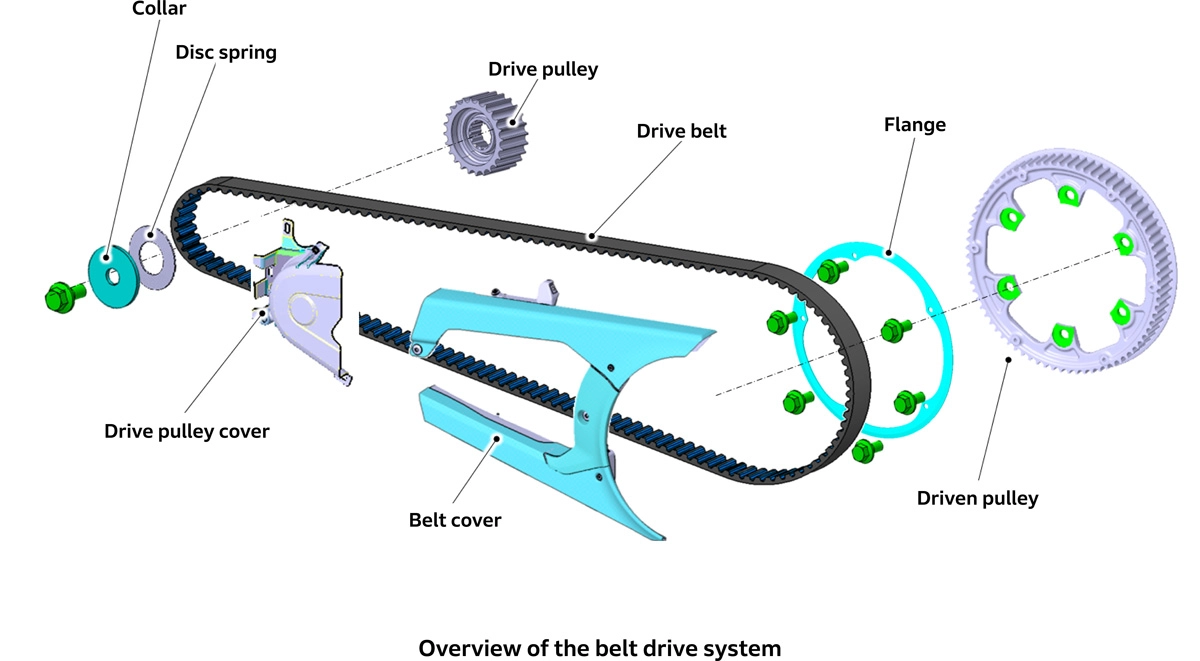
The belt drive system is also considered suitable for electric motorcycles in terms of maintenance. In chain drive systems, the structure of the chain causes elongation due to wear on parts during use, necessitating regular adjustments. In contrast, belts are integrally molded with a rubber tooth profile around a carbon core wire and generally do not elongate, eliminating the need for regular adjustments like those required for chains.
Chain drive systems require regular oil lubrication due to their structure in which metal parts rub against each other. However, belts have no such metal friction points, so oil lubrication is unnecessary. As a result of this, another feature of the belt drive system is its cleanliness; unlike chain drive systems, there is no need to worry about oil splashing or getting on clothing.
Regular belt inspections are necessary to check for abnormal tension (excessive looseness or tightness), entrapment of debris, or external damage. Unlike chains, however, belts do not require regular oil lubrication or tension adjustments, making reduced running costs a key advantage of belt drive systems.
The belt drive system also helps reduce weight by changing the primary drive system material from metal to rubber. However, the belt can be damaged if debris such as stones becomes lodged between it and the pulley. Therefore, belt covers has been installed to prevent such debris from entering.
There are other factors contributing to the improved quietness besides the belt. ICE vehicles often use spur gears in their power transmission mechanisms, which offer excellent transmission efficiency but generate significant noise when meshing. Therefore, the WN7 has adopted helical gears for quietness. In this way, the WN7 has improved quietness throughout the entire drive system.
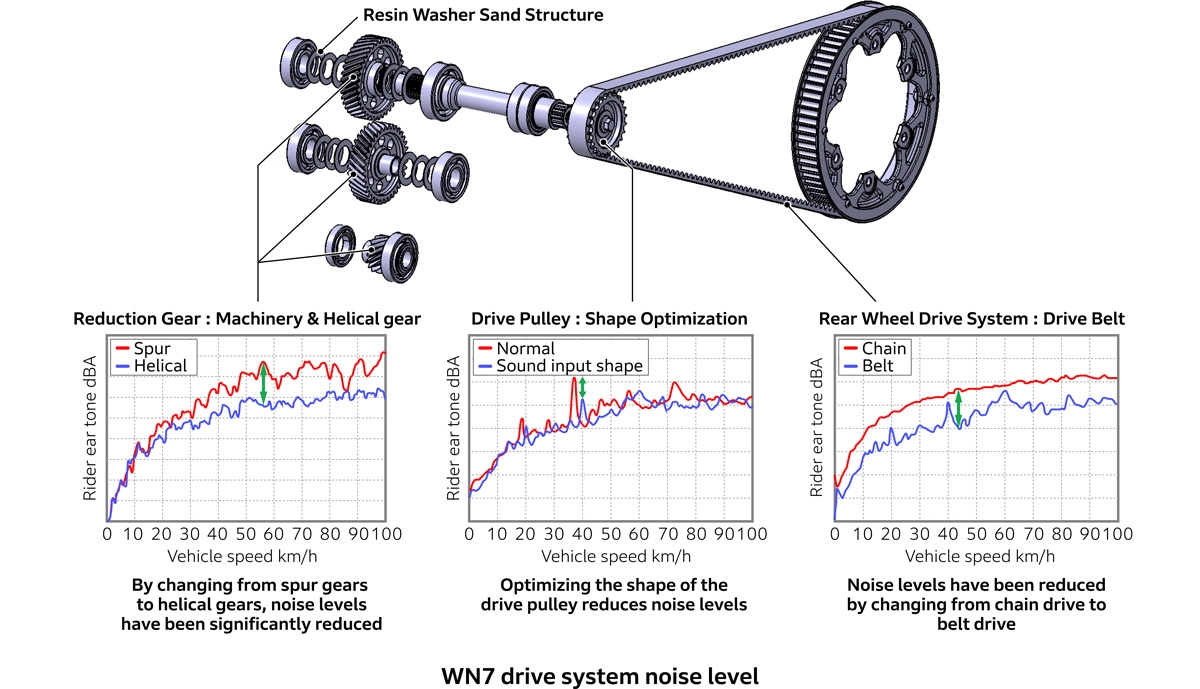
A lower center of gravity was achieved by having the shaft of the WN7’s water-cooled motor, which is mounted in a low position, extend out to the right side of the vehicle. From there, driving torque is transmitted upward through three gears, then returns via a shaft to the left side, where it is transferred to the belt drive system installed on the left. Concentrating components on the left side would have created an unbalanced weight distribution. Therefore, the heavy triple gear assembly was placed on the right side to achieve balance.
Features Supporting Comfortable Riding
Deceleration Power Selector
In addition to its split front-rear configuration without a main frame and its drive belt system, the WN7 also features a deceleration power selector. The WN7 leverages the motor’s inherent ability to freely control its regenerative deceleration capability, setting four levels of regenerative deceleration. These range from Level 0 (equivalent to neutral in an ICE vehicle) to Level 3 (strong regeneration).
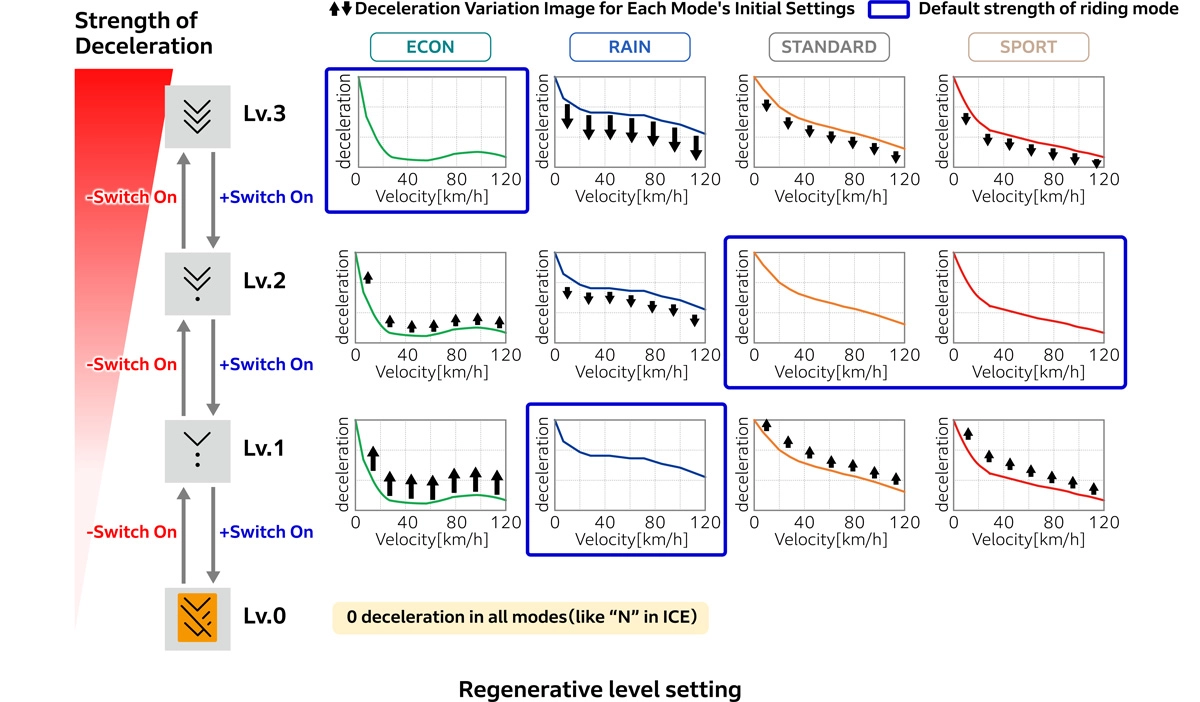
A default level is set for each riding mode: Level 3 for ECON, Level 1 for RAIN, and Level 2 for STANDARD and SPORT. On winding roads, increasing the regenerative deceleration level makes controlling acceleration and deceleration easy solely with the throttle, providing a more immersive experience. Conversely, when cruising on highways, lowering the regenerative deceleration level reduces the frequency of throttle adjustments, helping to reduce fatigue. This allows for usage tailored to the riding situation and preference.
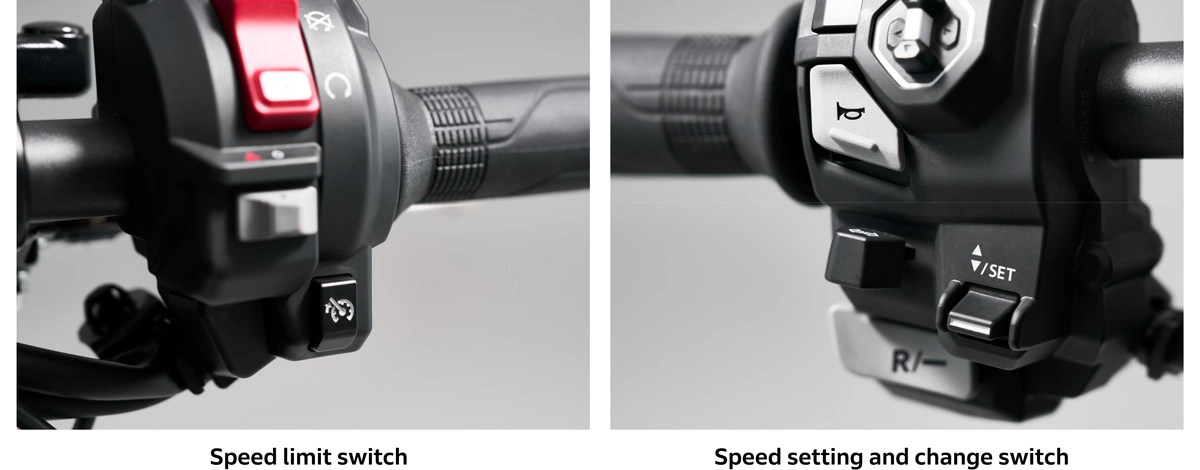
Operation is simple: just press the + (plus) and - (minus) switches located on the switch box on the left handle. Pressing the switch on the plus side will decrease the deceleration rate, and pressing the switch on the minus side will increase the deceleration rate. The current level is indicated by the number of arrows displayed on the meter.

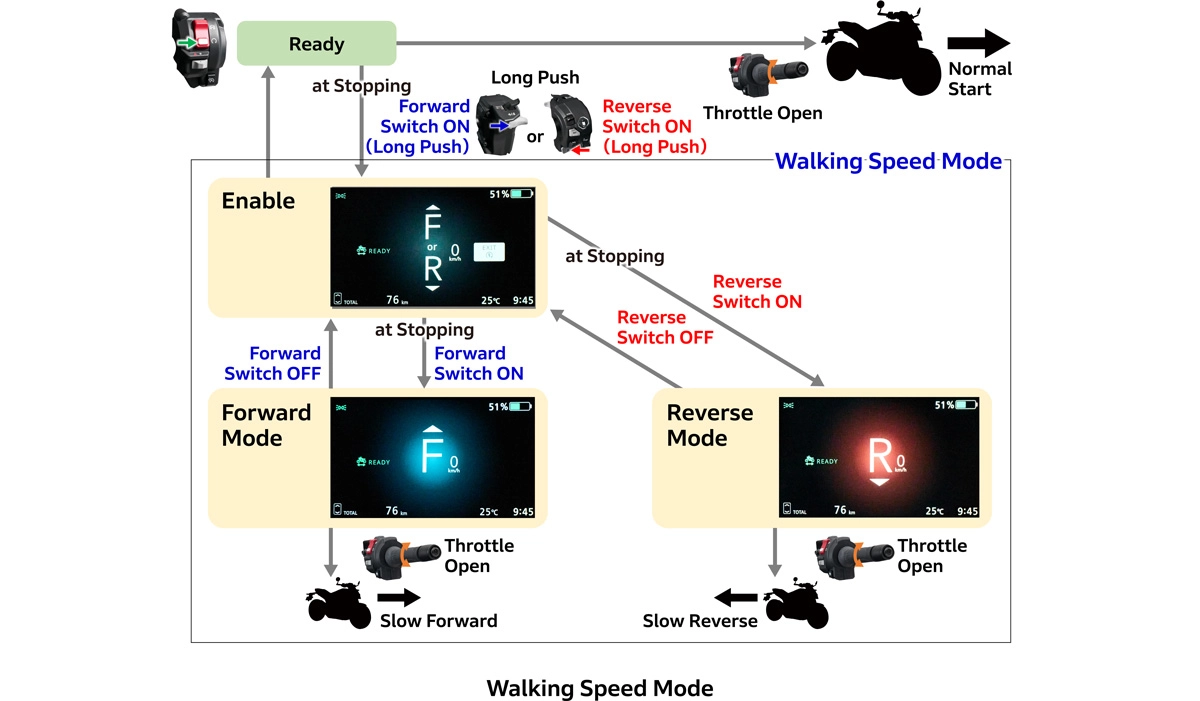
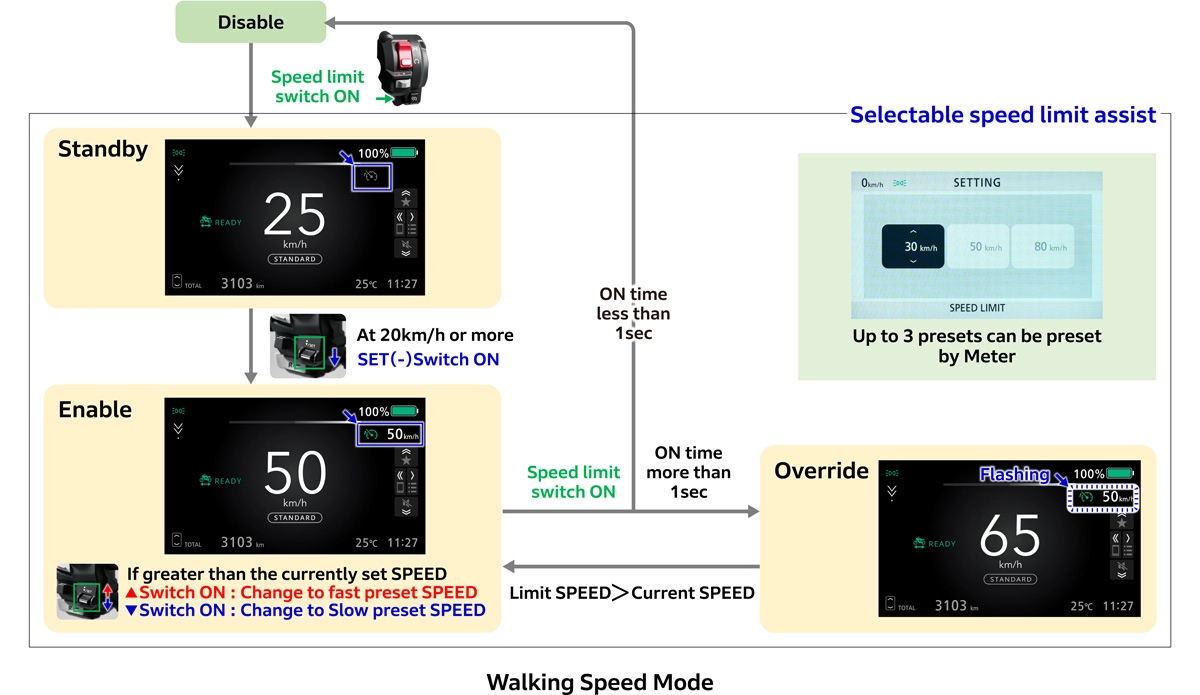
Walking Speed Mode
The WN7 also features a walking speed mode that assists moving the vehicle in tight spaces. Press and hold the plus switch while parked to activate slow forward mode, or press and hold the minus switch for slow reverse mode. This allows operation while straddling the vehicle without dismounting when parking and exiting. The throttle opening allows for speed adjustment, enabling the rider to make precise adjustments.
Selectable Speed Limit Assist
Selectable speed limit assist is a feature that allows riders to set a speed limit at any desired vehicle speed. Up to three speed limits can be set in increments of 1 km/h, starting from 20 km/h. In Europe, it’s common to encounter 30 km/h speed limits upon entering towns, which then change to 80 km/h limits upon exiting. It's also well-known that enforcement is strict.
Selectable speed limit assist upon entering a 30 km/h zone causes the WN7 to promptly decelerate to 30 km/h. Upon exiting the zone, pressing the switch and selecting a higher speed setting will return the motorcycle to the set speed. Using selectable speed limit assist allows for comfortable riding without worrying about speed limits. Pressing and holding the speed limit switch when overtaking or in other similar situations enables riding at speeds exceeding the set limit.
The WN7 is a new electric motorcycle that embodies over 75 years of Honda’s motorcycle development experience and expertise, designed to emphasize lightness and ease of handling in daily riding situations. Honda has incorporated a number of carefully thought-out technologies, aiming to deliver a smooth ride distinct from ICE models, while also achieving a high level of riding enjoyment and the thrill of the open road.



