ASIMO OS: Honda original vehicle operating system (OS)
The environment surrounding automobiles is now characterized by a trend toward electrification with the goal of realizing carbon neutrality, as well as growing expectations for so-called “software-defined vehicles (SDVs).” Such SDVs integrate intelligent and IT technologies and continue to advance in functions and performance even after the customer purchases the vehicle. The ASIMO OS (operating system), an original vehicle OS developed by Honda, has been attracting industry attention as the core of Honda SDVs.

As the name “operating system” suggests, a vehicle OS is fundamental software designed to control the vehicle’s onboard computers and, by extension, the entire vehicle. A vehicle OS integrally controls electronic control units (ECUs) and provides an environment for running various applications on the vehicle, just as the Android OS or iOS does for smartphones. Honda will install the ASIMO OS to Honda 0 Series*1 models, scheduled to be launched to the global market starting in 2026, and will continuously advance it as the core of Honda SDVs. The ASIMO OS will serve as the foundation for the operation of the Automated Driving/Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (AD/ADAS), integrated dynamics control that delivers the “joy of driving,” and digital user experience (Digital UX) that creates a new value of vehicles as a “space” for the users. Additionally, the ASIMO OS will connect to the cloud via networks, enabling a linkage to external information, software development and testing, and OTA (Over-The-Air) software updates.
ASIMO was a humanoid robot developed as part of Honda fundamental technology research with the aim of helping people, while coexisting with people in society. Honda began robotics research and development in 1986, and introduced ASIMO in 2000. ASIMO became an icon in the field of robotics from the 2000s through 2010s and was loved by people all over the world for a long period of time thereafter. Honda gave the name ASIMO to the vehicle OS, the core of its SDVs, with a determination to strive for making the Honda 0 Series an icon of next-generation EVs, which will surprise and inspire people all around the world, just as ASIMO did. Honda is developing SDVs unique only to Honda by further advancing ASIMO technologies, including those for recognition of external environments and autonomous behavior control technologies that enabled ASIMO to act while understanding the intentions of people around it, and by combining such robotics technologies with advanced AI technologies.
Let's take a look at what kind of cars Honda SDVs will be, and how they will be realized with the ASIMO OS at the core, and outline the SDV that Honda is aiming for.
*1 Honda 0 Series: A completely new EV series Honda is developing from “zero” with a “Thin, Light and Wise” development approach.
Honda SDVs: ultra-personalized vehicle that continues to advance and becomes more user-friendly through repeated use
Have you ever had the experience of using a family member or friend's smartphone only to find it surprisingly “difficult” to use? That is because everything from the installed apps to the layout of the home screen has been customized to the owner's preference. Then, when you go back to using your smartphone, you will once again appreciate its ease of use. Honda is envisioning to create SDVs which will continue to advance and become increasingly user-friendly through repeated use, just like smartphones. By sharing more time and experiences with the users, Honda SDVs will become ultra-personalized vehicles that understand and support their respective users better than any other vehicles in the world. Honda is striving to develop SDVs that not only offer continuous improvement of automated driving (AD) and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) to expand the joy and freedom of mobility, integrated control of vehicle dynamics to offer the joy of driving while feeling a sense of oneness with the vehicle, and digital UX to create new value of the EV as a “space” for people, but also advance to better accommodate preferences and needs of each and every customer through over-the-air (OTA) updates.
AD/ADAS that expands the joy and freedom of mobility

AD/ADAS is the area in which Honda is putting the most effort in the development of SDVs. Honda is striving to further expand the joy and freedom of mobility through the advancement and popularization of AD/ADAS. In 2021, Honda became the first company in the world to put the Traffic Jam Pilot function into practical use, where the system operates the accelerator, brake, and steering wheel on behalf of the human driver, under certain conditions, enabling not only hands-off but also eyes-off*2 driving.
In the field of ADAS, Honda has been advancing the functions and performance of Honda SENSING and is expanding the application of Honda SENSING 360, which expanded the range of sensing to provided omnidirectional*3 coverage around the vehicle, not just the front and rear of the vehicle. Based on these fundamental technologies and know-how, Honda is pursuing AD powered by AI that accurately recognizes and understands the vehicle’s surroundings and enables the system to behave like an experienced driver in a wide range of traffic environments and situations. To achieve such AD, Honda is further improving the level of automated driving using high-precision sensors and by integrating its technologies with the technologies of Helm.ai, a partner company that excels in AI image recognition. Honda is striving to become the world’s first automaker to enable eyes-off driving in all driving situations, including regular (non-expressway) roads.
Honda will also pursue the “ultra-personal optimization” of its AD/ADAS. The degree of acceleration/deceleration, steering speed, and other driving behaviors vary depending on the driver's preferences and driving skills. The AD/ADAS for future Honda SDVs will learn the driver's tendencies and become capable of executing, for example, gentle or agile overtaking. The system can also be adjusted to the driver's preference, such as whether to drive near the center of the lane or to the left or right while the lane keeping assist is activated. With such meticulous attention to detail, Honda aims to realize the ultra-personal optimization of AD/ADAS for each individual driver.
*2 In March 2021, Honda launched an all-new Legend sedan equipped with the Honda SENSING Elite featuring the Traffic Jam Pilot and other hands-off driver assistive functions.
*3 There is a limit to the detection capability of Honda SENSING 360, and it does not eliminate the need for visual confirmation by the human driver.
Integrated control of vehicle dynamics that offers the joy of driving
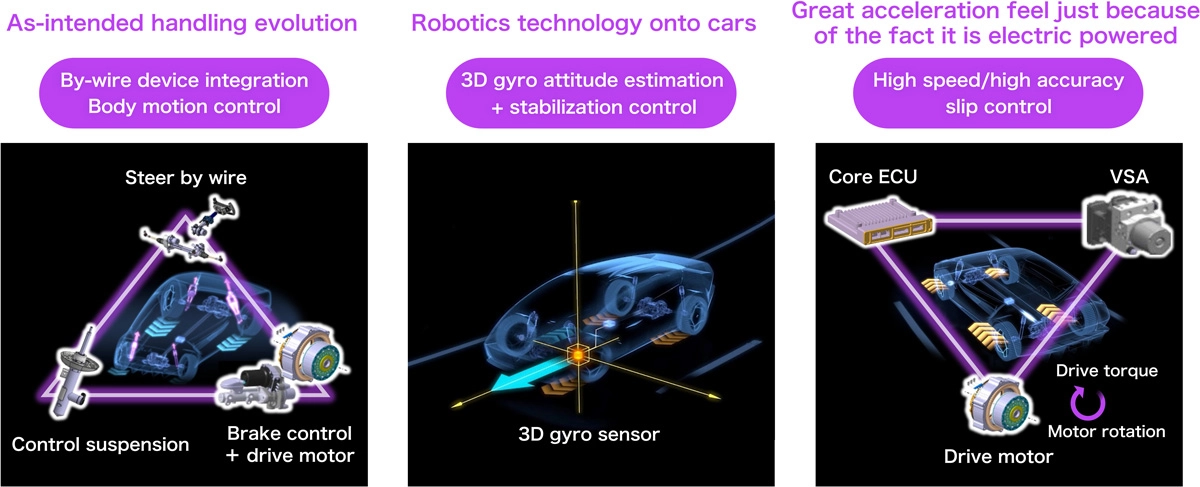
With the goal of enabling everyone to enjoy driving safely and with peace of mind, Honda SDVs will seamlessly link various control devices and realize integrated control of vehicle dynamics that offer the joy of driving. In addition to dynamics control technologies Honda has refined to date, such as Vehicle Stability Assist (VSA) and an Adaptive Damper System, Honda SDVs will utilize highly-sophisticated 3D gyro sensor-based, vehicle posture estimation and stabilization control technologies. Honda has amassed these technologies through the development of its original robotics technologies, applying integrated control of s steer-by-wire system, controlled suspensions, and other by-wire devices such as the e-Axle, a drive module. Moreover, by coordinating the drive torque control by the e-Axle and the brake control by the VSA, driving force of all four wheels is independently and precisely controlled, ensuring smooth acceleration even on slippery road surfaces. By applying these integrated controls and stabilizing the vehicle in various driving situations, Honda SDVs will realize vehicle behaviors at the will of the driver and offer the joy of driving with great peace of mind.
Also, the more the user drives their Honda SDV, the better the vehicle understands the driver's characteristics, skill level, and preferences. This will enable the vehicle to suggest a drive mode that best accommodates the driver's preference depending on the driving situation, and also offer an appropriate drive mode for the situation by estimating the road surface conditions based on information on the environment obtained from outside the vehicle from various on-board sensors such as cameras. The Honda vision for its SDVs is to accommodate the needs and preferences of each and every user and offer sporty driving and peace of mind in every driving situation.
Digital UX that creates a new value for EVs as a “space” for people’s mobility
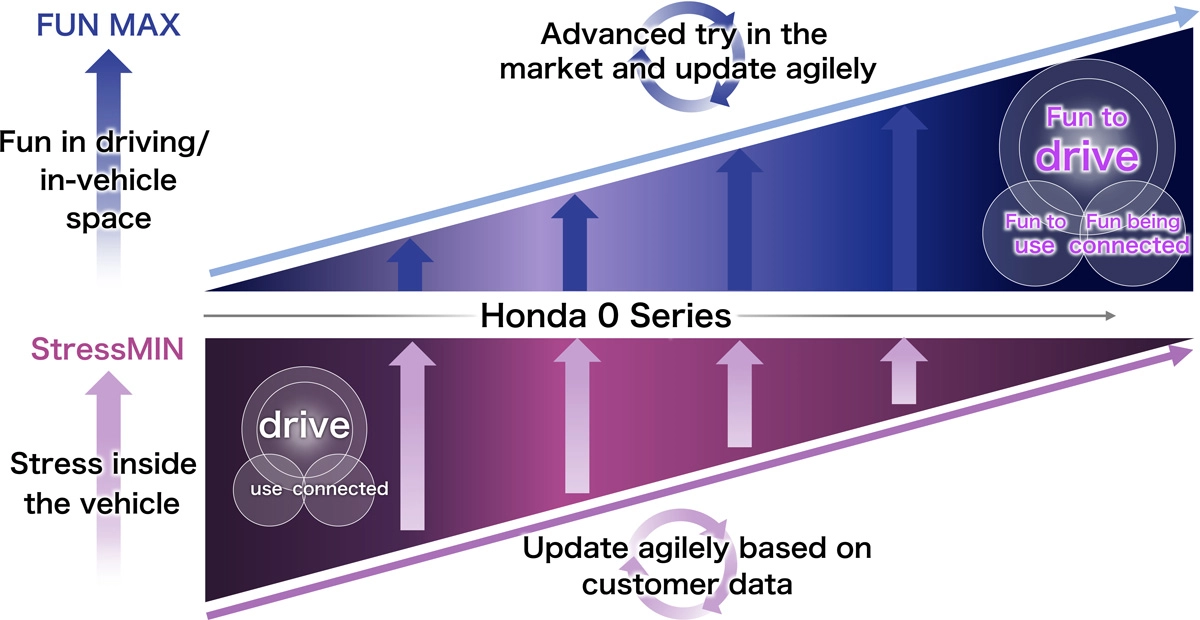
Another value that Honda is striving to offer with its SDVs is the creation of an attractive “space” for people’s mobility. In addition to minimizing various stresses related to the use of a car, such as driving and getting in and out of the vehicle, Honda SDVs will offer new value that maximizes the fun of using a car. To this end, Honda will further advance existing connected vehicle technologies and incorporate multimodal generation AI to utilize a variety of data obtained from cameras and other sensors inside and outside the vehicle to offer in-vehicle experiences that reflect the emotions and intentions of the occupants. Honda SDVs will proactively make suggestions that they deem most appropriate at the time. For example, when the user is taking a long drive with their pet, the vehicle will find pet-friendly cafes and restaurants and suggest the users to take a break; when the vehicle detects a crying child in the cabin, it will suggest to play music that would be fun for children; and the vehicle will suggest switching to a mode that prioritizes riding comfort in coordination with the integrated dynamics control technology.
The greatest features of the value of a Honda SDV as a “space” for people’s mobility is the fact that the more the user drives it, the more the vehicle advances to achieve the “ultra-personal optimization.” The AI accumulates a history of what the occupants have selected in various situations and, just like a smartphone’s predictive texting feature, the vehicle will make predictive suggestions. The more history the Honda SDV accumulates, in other words, the more the customer uses their vehicle, the better suggestions the vehicle will offer tailored to the preferences of the user. Honda SDVs will eventually grow to be a “partner” that understands the user the most and supports comfortable and convenient daily use of the vehicle.
Key technologies that realize Honda vision for SDVs
By tapping a phone number in a text message received on a smartphone, the user can instantly call the number, and by tapping a URL, the user can immediately access the website for purchasing that particular product. Smartphone users now take for granted the convenience of having various functions work together, but it is made possible by the fact that the apps work together on common basic software such as the Android OS and iOS. However, for automobiles, which involve the physical change of locations, the complexity of functional integration is far beyond that of smartphones. Through the independent development of the E&E architecture, which is the foundation of SDVs, the ASIMO OS, which is the basic software, and various applications, which run on the OS, Honda will realize advanced cross-domain control of a whole vehicle, which had been difficult until now, creating vehicles tailored to each and every user through “ultra-personal optimization.”
Centralized E&E Architecture comprehends all the data for the entire vehicle and provides functions

E&E architecture refers to the design and structure of the systems that connect the ECUs, sensors, actuators, and other devices installed in the vehicle. Most current vehicles domainize each function, such as AD/ADAS and dynamics control, and under the command of ECUs, which serve as the brains of each domain, functions such as sensing, operation of the accelerator and steering, and in-vehicle infotainment (IVI)*4 are realized for each domain (Domain E&E Architecture). While this type of E&E architecture excels in the efficiency of data transfer within a domain, there are several issues that needed to be addressed in order to improve software performance and speedy updates. There are certain limitations on the amount and speed of data sharing between domains, and when updating the software of one ECU, the software and communication contents of the related ECUs must also be changed.
For the 2026 Honda 0 Series models, Honda will adopt a Domain Centralized E&E Architecture, which will consolidate functions into three domains. Then, for the following generations of Honda 0 Series models, the Centralized E&E Architecture will apply centralized control by a single high-performance ECU. This type of E&E Architecture will make it possible to control each function using all the data for a whole vehicle, including data collected by cameras and radar inside and outside the vehicle, information from various sensors that monitor the vehicle's driving conditions, and information from sensors that detect vehicle operation by the driver.
*4 In-vehicle infotainment (IVI) is a collective name for in-vehicle systems that provide information and entertainment for the vehicle user.
Industry-leading high-performance SoC (System on Chip)

With the Centralized E/E Architecture, a single high-performance central ECU comprehends all the data for a whole vehicle and provides various functions and services. By 2030, AI performance requirements for SDVs are expected to be 500 times higher than that of 2024, and SoC capable of processing enormous amounts of data will be required for the central ECU. To realize the highest possible performance of its SDVs, Honda will co-develop a dedicated SoC with Renesas Electronics Corporation (hereafter referred to as Renesas).
This dedicated SoC will leverage the expertise of Renesas in chiplet technology*5 and integrate the AI accelerator optimized for original AI software developed by Honda, which enables customization to augment AI performance. Moreover, this SoC will achieve high integration by adopting the cutting-edge 3nm (nanometer) process*6 technology in semiconductor manufacturing. With these technologies, Honda and Renesas will target the world’s top-class 2000 TOPS (2,000 trillion operations per second)*7 level AI processing performance and 20 TOPS/W (20 trillion operations per watt)*8 power efficiency.
*5 Chiplet technology: A technology that manufactures integrated circuits by dividing them into multiple small chips (chiplets) and combining these chiplets to manufacture a single large-scale integrated circuit. It helps suppress yield loss, enables performance improvement through the addition of chiplets, and allows for customization through reconfiguration.
*6 3nm (nanometer) process: A semiconductor design and manufacturing method where the circuit line width is set to 3nm. The smaller the number, the more it allows for miniaturization, improving performance per unit area. 1nm is one billionth of a meter, or one millionth of a millimeter.
*7 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second): A unit used to represent the performance of AI processing, indicating how many trillion integer arithmetic can be performed per second. This target value refers to the result from executing a spare AI model.
*8 TOPS/W: Processing speed per watt of power consumption. The higher the number, the lower the power consumption.
AI technology that realizes Level 3 automated driving (eyes-off)
AI-powered image recognition demonstration
AI-generated image (top left) with categorization of subjects and recognition of the vehicle’s direction of travel based on an in-vehicle camera image (top right), and a bird's-eye view LiDAR image (bottom left), and front view LiDAR image (bottom right)
Traffic Jam Pilot, which Honda put into practical use in 2021, is the world's first technology that enables the driver to take their eyes off the road while driving (eyes-off), and qualified for Level 3 (eyes-off) automated driving (conditional automated driving in a limited area)*9, which allows the system to drive the vehicle instead of the human driver under certain conditions. Level 3 automation is only one level above Level 2 (partial driving automation), however, the level of technical difficulty is significantly different between Level 2, with the human driver primarily responsible for driving, and Level 3, with the system taking over the primary driving role, enabling the driver to take eyes off the road under certain conditions. This is because Level 3 requires the system to correctly recognize and understand various driving situations that may occur in a real-world traffic environment, and to perform appropriate operations to avoid collisions. In other words, the system must completely eliminate traffic accidents that people think a “human driver could avoid.” To achieve Level 3 on all roads, including non-expressway roads, the system must be able to correctly recognize, understand and deal with other road users, including pedestrians abruptly crossing the road in front of the vehicle or motorcycles and bicycles that quickly approach the vehicle from behind trying to weave through traffic. By combining Honda technology and knowledge established in the development of the Honda SENSING Elite with the AI-based image recognition technology of Helm.ai, Honda is striving to become the world’s first automaker to enable Level 3 automated driving in all driving situations, including regular (non-expressway) roads.
The AI-based image recognition technology of Helm.ai is being developed with “unsupervised learning” as well as “deep teaching” that dramatically advances the unsupervised learning method. Unlike supervised learning, where the machine learns from image data labeled by people, unsupervised learning lets the machine learn without being provided with the correct answers and derives the patterns and unique characteristics of the unlabeled data on its own. As one example, this enables the vehicle to recognize all types of trees that change appearance depending on the season more abstractly as “roadside” trees, thereby recognizing the road it should stay on even if the white road lines/marks aren’t visible. Another example is how, without labeling an image of a deer as an “animal,” the AI will recognize it as an animal on its own and perform appropriate control, such as collision avoidance.
In addition to combining its technology for the recognition of external environments, established through the development of Honda SENSING Elite, together with the AI-based image recognition technology of Helm.ai, Honda will collect driving data on a global basis and let the AI learn from it. This also will combine the risk assessment models of experienced drivers to realize AD that provides the occupants with great peace of mind as if the vehicle is being manually driven by an experienced human driver, even on a road where the vehicle has never been before. In addition, Honda will apply its original cooperative AI technology to further improve the precision of cooperative behavior, such as yielding the right of way to others on the road, which is difficult even for a human driver.
*9 Level of driving automation defined (J3016) by SAE International (the U.S.-based global standards development and professional association of engineers and technical experts in mobility engineering.)
Multimodal generative AI technology that enables ultra-personal optimization of vehicle functions and performance
Differences between singlemodal AI and multimodal AI
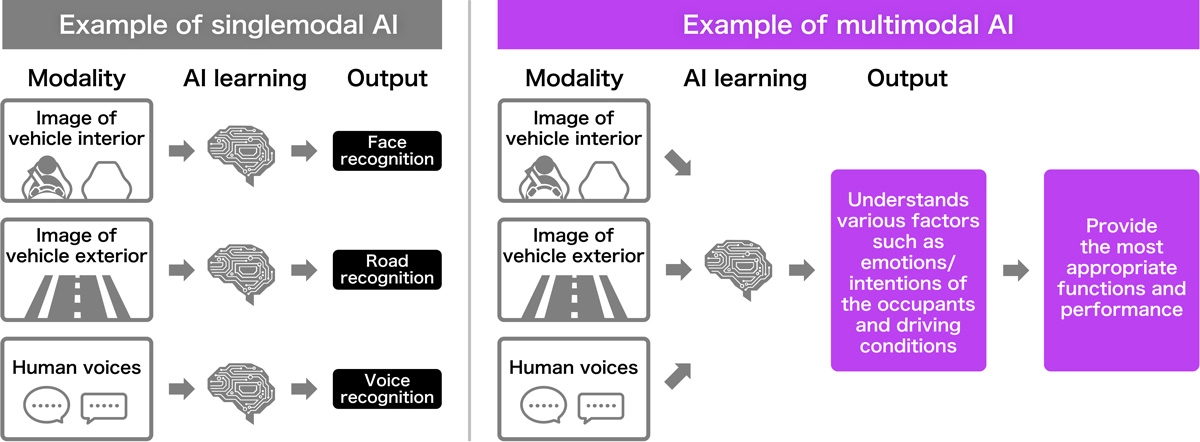
Conventional AI generally processes information based on a single modality (type of information), such as images or sounds, but real humans think, judge, and act based on multiple modalities, such as visual, auditory and tactile sensations. Honda is aiming to equip its SDVs with multimodal generative AI that collects information from two or more modalities to make inferences, just as humans do. This will enable the vehicle to make optimal suggestions based on a deeper understanding of the occupants’ emotions and intentions, as well as the situation the vehicle is in and the driving conditions. For example, the system can accurately estimate that “a child is crying” from the video and audio inside the vehicle and suggest changes to the vehicle's interior environment.
Virtual development environment dramatically increases the speed of software development and market launch
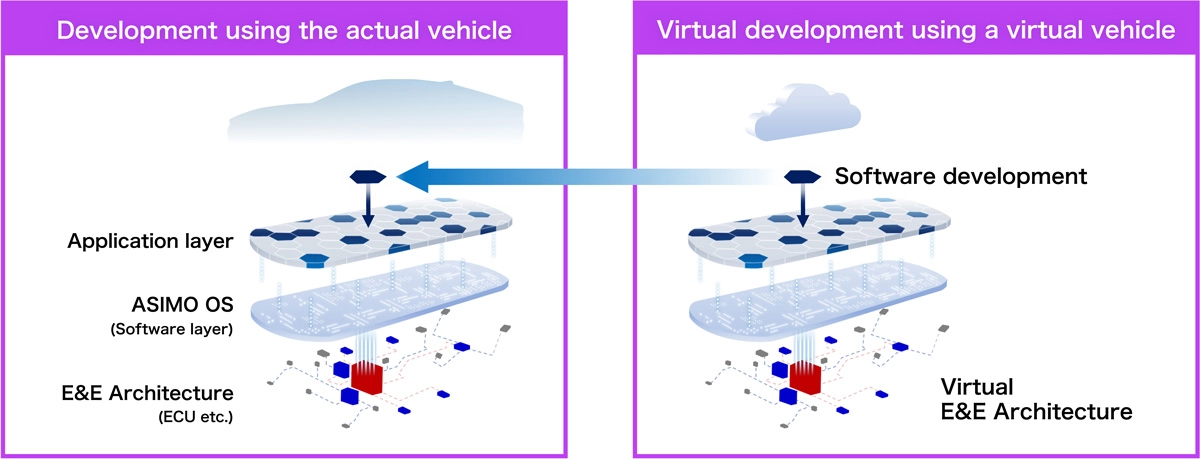
The importance of software increases exponentially for SDVs, which feature the Centralized E&E Architecture and high-performance SoC to centrally control the vehicle. In order to develop and launch the latest functions for its SDVs as quickly as possible, Honda will establish a virtual development environment where software development and in-vehicle testing can be done virtually.
In traditional hardware-driven development, it was common to develop software, wait for the completion of the ECU to install it, and then install the ECU in an actual vehicle and conduct validation and make necessary adjustments. In a virtual development environment, however, virtual ECU is created on a computer, enabling software development to proceed without waiting for the completion of the ECU. Moreover, the software developed in this way can be installed on a virtual vehicle for validation. Since the vehicle is virtual, testing can be conducted on 100 or even 1,000 vehicles simultaneously. This approach dramatically accelerates software development and can be utilized not only for installing software in new vehicles, but also for software updates for vehicles already in the market.


