Honda SENSING 360+, Honda SENSING 360, Honda SENSINGAdaptive Driving Beam

Technology overview
Automatically controlling the illumination area for better vision and greater comfort using original light distribution based on actual accidents involving pedestrians
A thoroughly researched much-needed function for night vision
A variable high beam system split into upper and lower sections detects vehicles in front and oncoming vehicles and automatically controls the illumination area accordingly to minimize glare for other drivers. The system was developed to provide excellent visibility, helping to minimize night-time accidents involving pedestrians and make it easier for the driver to see the shape of the road. This was done by expanding the illumination area while taking into consideration the glare created for not only vehicles ahead, but also pedestrians.
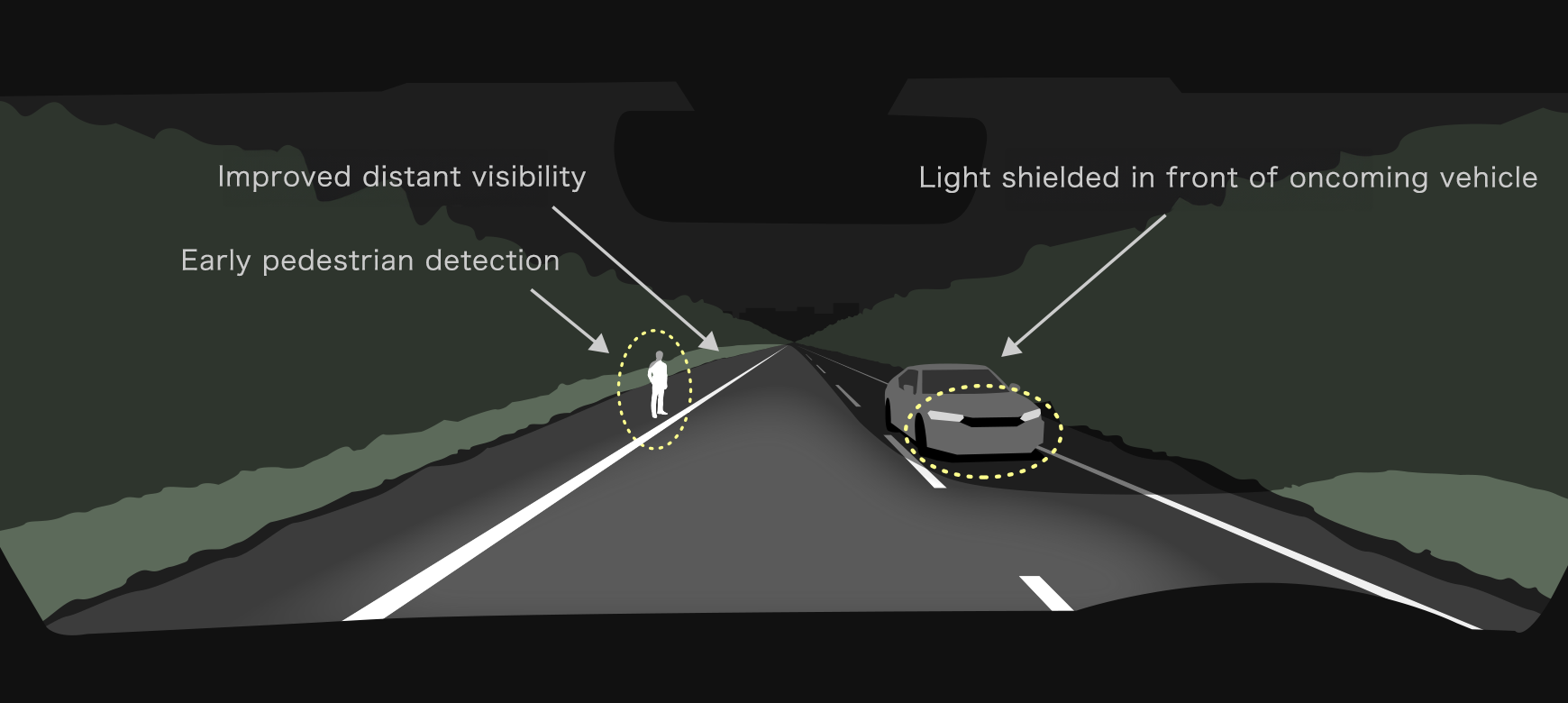
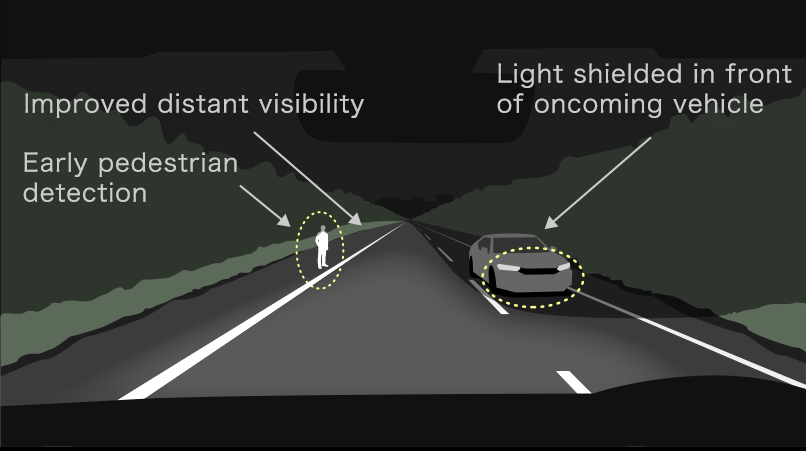
How it works
Adaptive Driving Beam light configuration and roles
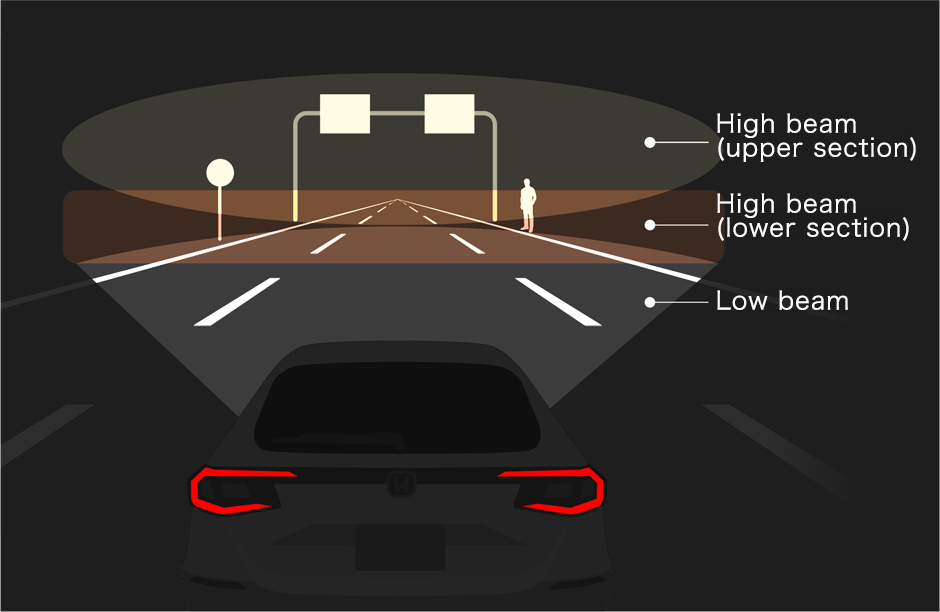
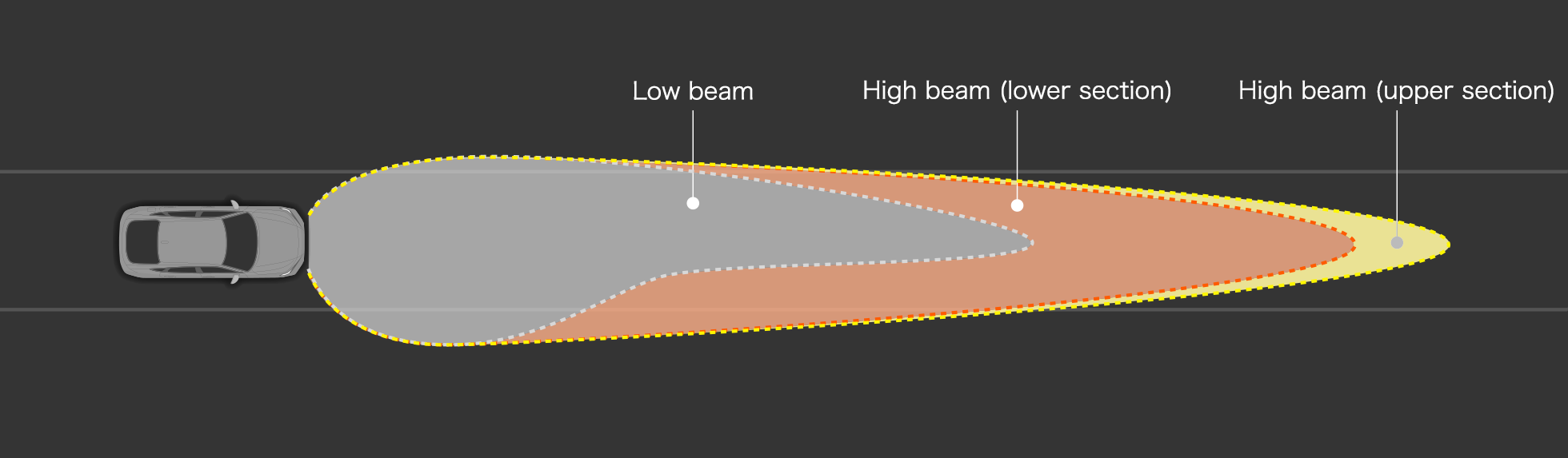
High beam (upper section)
- High beam directed at an elevated height
- Light distribution designed to allow the driver to see up higher by clearly illuminating distant areas
- Switches on when there are few street lights or other lights up ahead, and there are no vehicles forward of the user’s vehicle
High beam (lower section)
- High beam directed at a low height combining light partitioned into multiple zones
- Light distribution designed to both clearly illuminate distant areas, ensuring visibility for early pedestrian detection, and mitigate glare for pedestrians
- Light distribution area partially extinguished when there are vehicles forward of the user’s vehicle to minimize glare for the other drivers
Conditions for activation
Adaptive Driving Beam is activated at night when the light switch is on Auto and the light switch lever is in the low beam position.
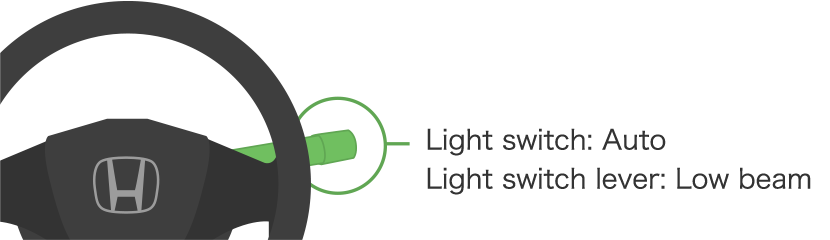
Adaptive Driving Beam on-off switching
If there is no vehicle in front…
-
STEP1
Engine start
Low beam switches on.

-
STEP2
Over 10 km/h
High beam (lower section) switches on.

-
STEP3
Medium/high speed driving
High beam (upper section) switches on if there are few street lights or other lights up ahead.

-
STEP4
Deceleration below 24 km/h
High beam (upper section) switches off.

-
STEP5
Deceleration below 6 km/h
High beam (lower section) switches off.

If there is a vehicle in front…
-
STEP1
Engine start
Low beam switches on.

-
STEP2
Over 10 km/h
High beam (lower section) switches on in parts.

-
STEP3
Medium/high speed driving
High beam (lower section) stays on in parts.

-
STEP4
Deceleration below 24 km/h
High beam (lower section) stays on in parts.

-
STEP5
Deceleration below 6 km/h
High beam (lower section) switches off.

Even if there is a vehicle in front and high beam (lower section) is only partially on, the high beam indicator stays on.
Commitment of Honda
Development of Adaptive Driving Beam started with a desire to reduce the number of accidents by improving the visibility achieved with headlights given that an overwhelming number of accidents in which a pedestrian crossing the road died occurred at night and 90 percent of such accidents occurred when the headlights were only on low beam*1. We designed the light distribution based on analysis of actual accident data.
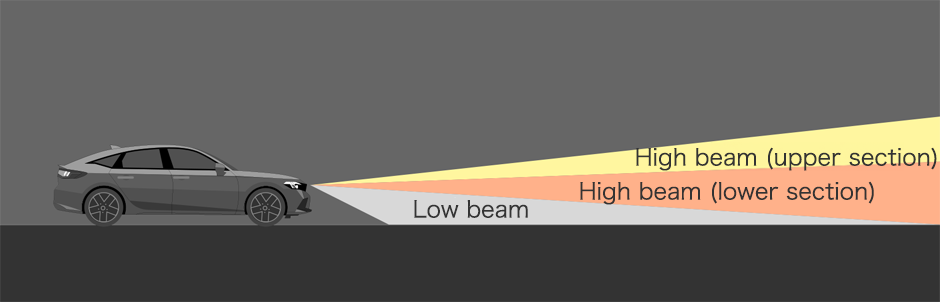
Illumination ranges of each beam
Characteristics of night-time accidents involving a pedestrian death
- 90 percent of accidents in which a pedestrian crossing the road dies occur when headlights are only on low beam*1
- Many occur near intersections when going straight ahead and on straight roads
- Many fatal accidents occur at a speed between 40 and 60 km/h
- Around 60 percent of all accidents involving pedestrians occur at a speed no higher than 20 km/h*2
- The majority occur in urban areas.
Based on these characteristics, we can expect to be able to minimize the number of accidents by making Adaptive Driving Beam function from a low speed. We have also designed light distribution of the high beam (lower section) based on light distribution research that determined the brightness required to detect a pedestrian.
- *1 National Police Agency website traffic accident data, 2016
- *2 Institute for Traffic Accident Research and Data Analysis (ITARDA), 2014
Researching what drivers want to see
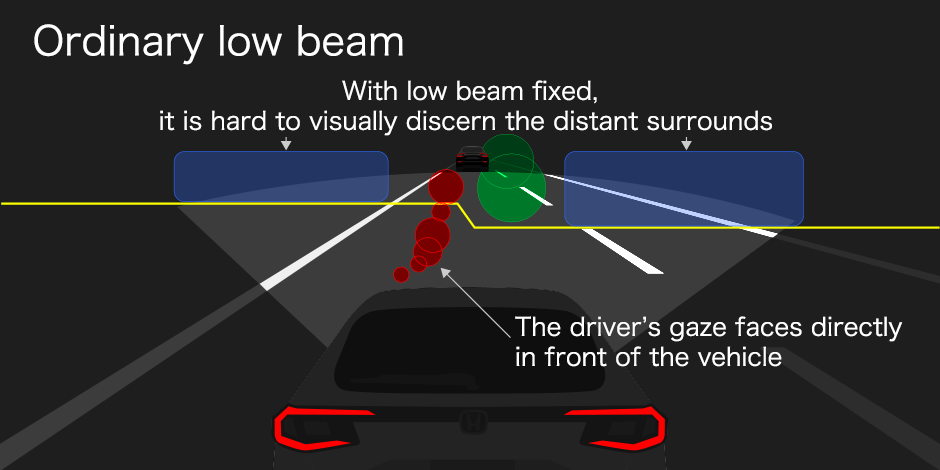
Using eye tracking systems, we have conducted research to determine what drivers are trying to see. Recreating a situation where there are vehicles oncoming and in front, and fixing the headlights on low beam, we found the driver’s gaze is agitated, busy trying to acquire information. Conducting the same experiment again using Adaptive Driving Beam, the driver’s gaze stays in the center as they can see what they want to see and their driving is stable.
Driver’s gaze with ordinary low beam and Adaptive Driving Beam
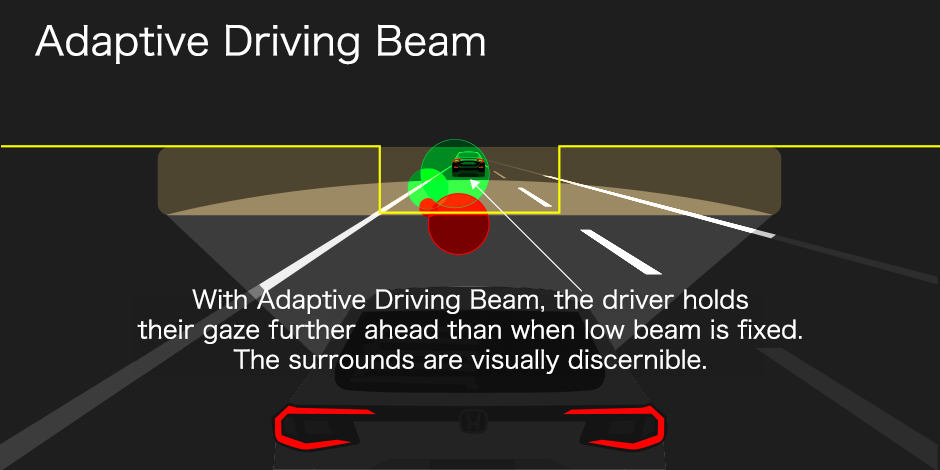
Alleviating concerns and discomfort about high beam glare
Through research, we learned that drivers have fundamental concerns about the glare high beam creates for other vehicles, cyclists and pedestrians, and concerns about illuminating surrounding houses in residential areas.
Because many accidents involving pedestrians occur in urban areas, we believed that a high beam that made pedestrians more visible while alleviating such concerns and discomfort would be a valuable safety feature. The high beam (lower section) was therefore introduced as an original Honda beam.
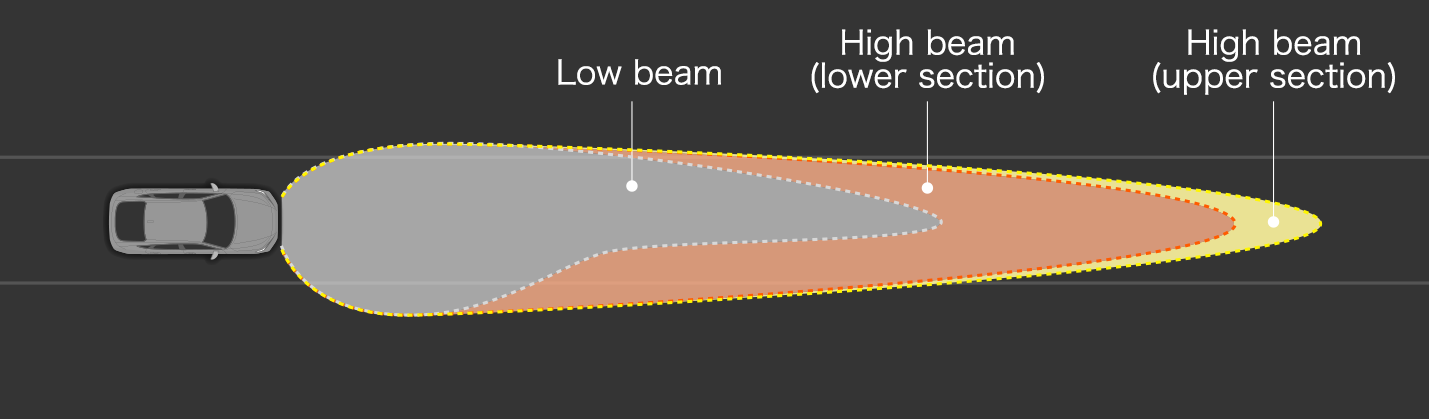
Adaptive Driving Beam comparison with vehicle in front (illumination area illustration)
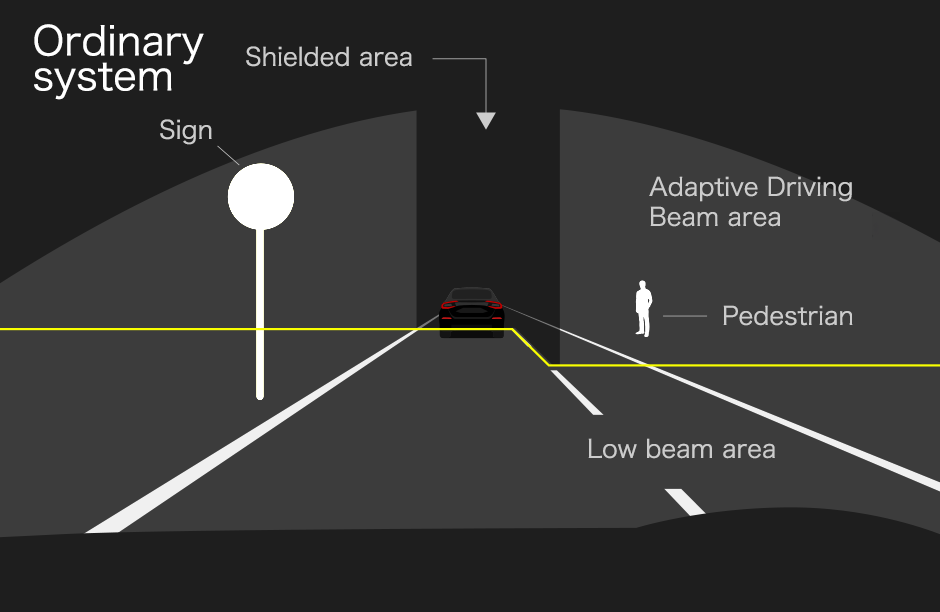
Ordinary high beams are tall, creating glare for pedestrians. Glare also affects drivers when light is reflected off signs in an elevated position.
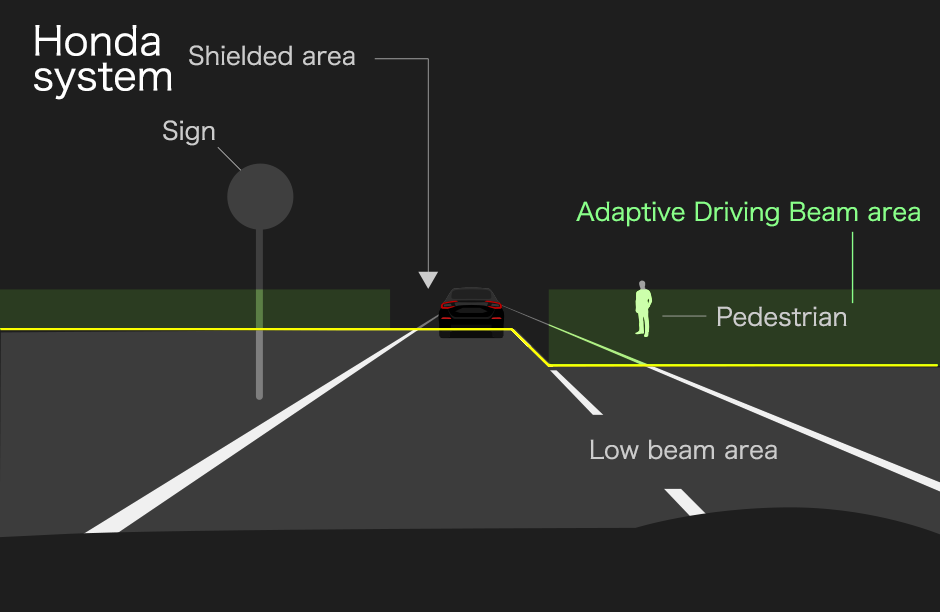
Honda’s high beam (lower section) illuminates to a low height, reducing glare for pedestrians and reducing the reflection of light off signs in an elevated position.
[Video] Functions image
The individual functions of the driver-assistive system have limited capabilities (e.g. recognition capability and control capability). Please do not overestimate the capabilities of any function and drive safely while paying constant attention to the vehicle’s surroundings. A system may not work or perform adequately depending on road conditions, weather conditions and vehicle conditions.
Function is not installed in some areas.
Depending on the model and timing of the market launch of the model, descriptions provided on this page and the actual functions available on customers’ vehicles may be different. For the functions available for each vehicle, please check the owners’ manual of the respective vehicle.
Related Contents
TechnologyAdaptive Driving Beam



