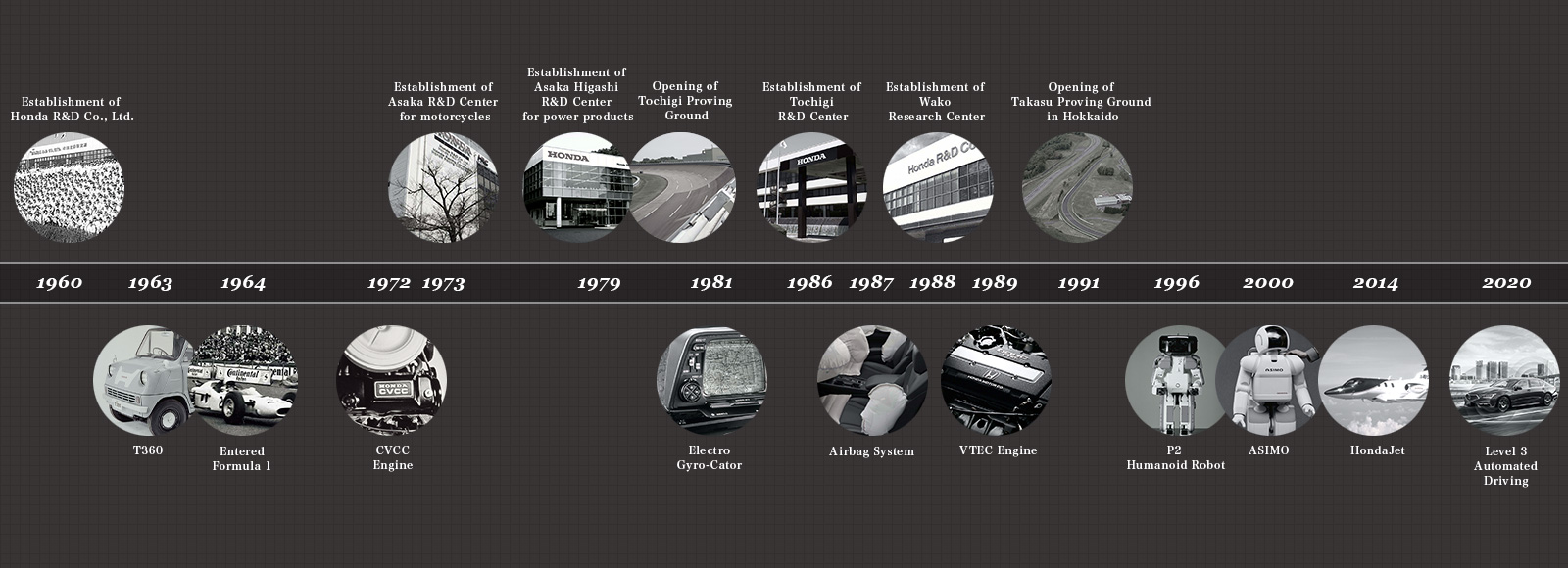
History
1960

1960 – Honda R&D Co., Ltd. was established as an independent company, separated from Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Promoted by Takeo Fujisawa, Honda R&D was created as a standalone research organization to develop technologies truly needed by society, without focusing on short-term profits, and to nurture them carefully over time. It is located within the Shirako Factory grounds in Wako City, Saitama Prefecture.
1963

1963 – T360
Honda’s first mass-produced automobile was the T360 mini truck. With a high-revving, high-output DOHC engine producing 30 PS at 8,500 rpm and delivering performance on par with sports cars, it made a major impact on the market.
1964

1964 – Entered Formula 1
Despite being the last entrant among Japanese automakers into the four-wheel market, Honda took on the challenge of competing in the world’s premier racing category, Formula 1. Honda R&D was responsible for developing and producing the race cars, achieving its first victory in only its second year of participation.
1972

1972 – CVCC Engine
Honda developed the world’s first engine to meet the stringent U.S. Clean Air Act (the “Muskie Act”) enacted in 1970. Installed in the Civic, Honda’s CVCC technology was shared with other automakers as part of Honda’s open approach to air pollution control technology.
1973

1973 – Establishment of Asaka R&D Center for motorcycles
A dedicated research center for motorcycle development was established. Later, the facility grew to include race development functions, creating machines like the “NR Block” that conquered the premier class of the Road Racing World Championship (now MotoGP).
1979

1979 – Establishment of Asaka Higashi R&D Center for power products
From generators to large outboard motors, storage batteries and Mobile Power Pack, which are key electrification products, this center has created a wide range of products and become a driving force delivering power worldwide.
1979

1979 – Opening of Tochigi Proving Ground
Honda’s unique test course for four-wheel vehicles, motorcycles, and power products such as lawn mowers and tillers. Spanning 1.41 km², it contains over 40 types of courses totaling 74 km in length.
1981

1981 – Electro Gyro-Cator
Before GPS was available, Honda successfully developed a system using a gyroscope and distance sensors to electronically determine the vehicle’s position. “Honda Electro Gyro-Cator” was developed to overlay that data onto a map displayed on the screen.
1986

1986 – Establishment Tochigi R&D Center
Created as a dedicated base for four-wheel research and development in line with the expansion of Honda’s automotive business.
1987

1987 – Airbag System
Honda developed Japan’s first driver-side SRS airbag system for domestic vehicles, introduced in the Legend, and has continued to advance safety technologies based on real-world accident analysis.
1988

1988 – Establishment Wako Research Center
A hub for fundamental research in advanced technologies such as aviation and robotics, producing innovative products including the HondaJet and ASIMO.
1989

1989 – VTEC Engine
The world’s first Variable Valve Timing & Lift Electronic Control System (VTEC), delivering improvements in power, acceleration, environmental performance, and drivability. First installed in the Integra in April 1989.
1991

1991 – Opening of Takasu Proving Ground in Hokkaido
A cold-climate test facility covering a vast area of 7.89 km², more than five times larger than the Tochigi Proving Ground, faithfully reproducing 54 types of roads from around the world.
1996

1996 – P2 Humanoid Robot
The world’s first fully autonomous, two-legged humanoid walking robot. Using wireless technology, all necessary devices were integrated into the torso. This enabled independent walking, ascending and descending stairs, pushing a cart, and other operations without wires, allowing for independent operation.
2000

2000 – ASIMO
The world’s first fully developed biped humanoid robot, achieving significant size and weight reduction from prototypes P2 and P3. ASIMO’s control technologies have been widely applied in robotics and mobility fields.
2014

2014 – First flight of HondaJet mass-production model
Featuring over-the-wing engine mount configuration, breaking with conventional aircraft design to achieve greater cabin space, reduced aerodynamic drag, and improved fuel efficiency.
2020

2020 – World’s first Type Designation for Level 3 Automated Driving
Approved by Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism for a system capable of performing driving operations under certain conditions, such as highway traffic jams.